Page 284 - MATHEMATICS COURSE FOR SECONDARY SCHOOLS BOOK 2
P. 284
The coordinates of the starting point can also be obtained from calculation by subtracting column matrices.
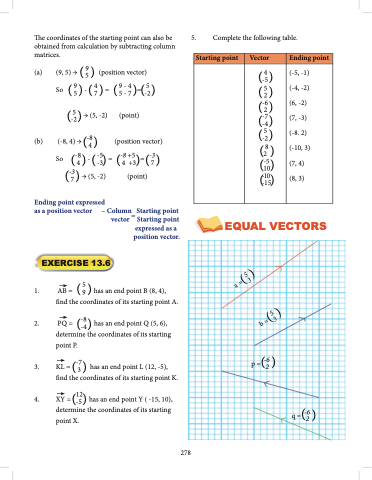
5.
Complete the following table.
Starting point
Vector
Ending point
(4 ) -5
( 52 )
(-6)
(2 ) -4
-7
(5 ) -2
(28 )
(-5) 10
() -15
-10
(-5, -1) (-4, -2) (6, -2) (7, -3) (-8. 2) (-10, 3) (7, 4) (8, 3)
(a)
(b)
(9, 5) → (59 ) (position vector) So - = =
(9 ) (4 )
5 7 5 - 7 -2
( 5 ) → (5, -2) -2
(-8, 4) → (-8 ) 4
()()( )() 4 -3 4+3 7
(-3 ) → (5, -2) (point) 7
-8 +5 -3 So - = =
-8 -5
Ending point expressed
as a position vector – Column Starting point
(9 - 4 ) (5 )
(point) (position vector)
1. 2.
3. 4.
AB = ( 59 ) has an end point B (8, 4), find the coordinates of its starting point A.
KL = 3 has an end point L (12, -5), (-7)
find the coordinates of its starting point K.
XY = 12 has an end point Y ( -15, 10), ()
vector = Starting point expressed as a
position vector.
EQUAL VECTORS
EXERCISE 13.6
(-8) -4
PQ =
determine the coordinates of its starting point P.
has an end point Q (5, 6),
-5
determine the coordinates of its starting
point X.
278
a = ( 35 )
b = ( 53 )
p =( )
-6
2
q =( )
-6
2