Page 3 - Amputation Prevention Centers - A White Paper
P. 3
Introduction The Diabetes Epidemic
ost hospitals face the challenge of determin- For the hospital, these centers result in n 2014, the Centers for Disease Control and In 2010, 1.9 million Americans were newly
Ming the best ways to invest limited capital additional revenue from procedures and patient IPrevention (CDC) estimated that more than diagnosed with diabetes mellitus. As this trend
and human resources in programs and services visits. However, these traditional models have 29 million adults in the U.S. had diabetes and continues to rise, the plausible threat of diabetic
that will not only meet their mission, but also seen increased scrutiny from Medicare and an additional 86 million more had prediabetes. foot infection becomes even more substantial
2
help maintain financial viability. However, hospitals other payers, along with denials and reductions About 60 percent of non-traumatic lower limb with dire financial consequences and severe limb
that have service lines with dedicated operations in revenue. For wound care service lines to amputations occur in those with diabetes. 3 and life-threatening outcomes. 5
teams and support of senior leadership have remain profitable, hospitals will need to adapt
been successful in tackling this challenge. In to these changes. Up to 25% of those with diabetes will develop a The World Health Organization has stated
4
addition, successful service lines have the foot ulcer in their lifetime. The most common that 80% of diabetes-related amputations are
8
following key elements: Creating a specialty center focused on one reason for hospital admission for diabetes is a preventable. Given the dire prognosis after
segment of the wound care population — the lower extremity complication. About one-third amputation, more should be done to ensure
5
• Strong clinical and administrative leadership
diabetic foot ulcer patient at risk for amputa- of the total direct costs of diabetes in the U.S. limb salvage. After a lower extremity amputa-
(that drives provider engagement)
tion — can be a solution for shrinking margins. are spent on lower extremity complications. In tion, 50% of patients will undergo a contralateral
6
• Care management across the continuum
Aligning with surgeons who specialize in limb addition, two-thirds of these lower extremity- amputation within 1-3 years. The mortality rate
9
• A strong referral base
salvage and building a comprehensive service related costs are due to hospitalizations because after major limb loss is alarming with a 5-year
• Superior customer service and positive
line around these champions can: most patients enter the hospital with an infection. 7 relative mortality of 70%, which is higher than
patient outcomes 1 10
• Increase hospital revenue many cancers.
®
RestorixHealth’s Amputation Prevention Center • Decrease major amputation rates
model, operating under the umbrella network • Improve population health
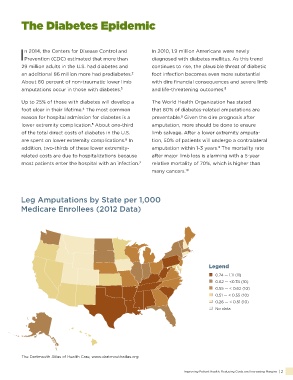
called the Amputation Prevention Centers of Leg Amputations by State per 1,000
America®, helps hospitals meet all of these goals.
Medicare Enrollees (2012 Data)
Hospital-based wound care centers emerged
in the late 1980s and continue to grow today.
These specialized centers make it easier for
patients with debilitating, painful non-healing
wounds and ulcers to recover.
“ Legend
“Every 30 seconds,
0.74 — 1.11 (11)
somewhere in the
0.55 — < 0.62 (10)
world, a limb is lost 0.62 — <0.74 (10)
0.51 — < 0.55 (10)
as a consequence 0.26 — < 0.51 (10)
of diabetes.” No data
— Cover of The Lancet, November 12, 2005
The Dartmouth Atlas of Health Care, www.dartmouthatlas.org
1 | Promoting Service Line Success by creating an Amputation Prevention Center ® Improving Patient Health, Reducing Costs and Increasing Margins | 2