Page 169 - Medicine and Surgery
P. 169
P1: KOA
BLUK007-04 BLUK007-Kendall May 25, 2005 7:57 Char Count= 0
Chapter 4: Disorders of the small bowel 165
Incidence due to ulceration of the adjacent ileum. Intestinal ob-
2% of the population, the most common congenital ab- struction may result from intussusception of the diver-
normality of the GI tract. ticulum or from a volvulus.
Age Investigations
Congenital Presence of gastric mucosa can be detected by scintiscan-
ning with 99m Tc labelled sodium pertechnetate, which is
Sex taken up by parietal cells (the Meckel’s scan).
2M > 1F
Management
Symptomatic Meckel’s diverticula are excised by wedge
Aetiology
resection.
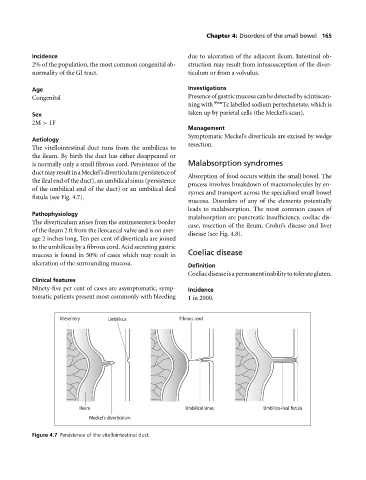
The vitellointestinal duct runs from the umbilicus to
the ileum. By birth the duct has either disappeared or
is normally only a small fibrous cord. Persistence of the Malabsorption syndromes
ductmayresultinaMeckel’sdiverticulum(persistenceof
Absorption of food occurs within the small bowel. The
the ileal end of the duct), an umbilical sinus (persistence
process involves breakdown of macromolecules by en-
of the umbilical end of the duct) or an umbilical ileal
zymes and transport across the specialised small bowel
fistula (see Fig. 4.7).
mucosa. Disorders of any of the elements potentially
leads to malabsorption. The most common causes of
Pathophysiology
malabsorption are pancreatic insufficiency, coeliac dis-
The diverticulum arises from the antimesenteric border
ease, resection of the ileum, Crohn’s disease and liver
of the ileum 2 ft from the ileocaecal valve and is on aver-
disease (see Fig. 4.8).
age 2 inches long. Ten per cent of diverticula are joined
to the umbilicus by a fibrous cord. Acid secreting gastric
mucosa is found in 50% of cases which may result in Coeliac disease
ulceration of the surrounding mucosa. Definition
Coeliacdiseaseisapermanentinabilitytotolerategluten.
Clinical features
Ninety-five per cent of cases are asymptomatic, symp- Incidence
tomatic patients present most commonly with bleeding 1in 2000.
Mesentery Umbilicus Fibrous cord
Ileum Umbilical sinus Umbilico-ileal fistula
Meckel's diverticulum
Figure 4.7 Persistence of the vitellointestinal duct.