Page 12 - Year 4 Maths Mastery
P. 12
Teaching for Mastery: Questions, tasks and activities to support assessment
Addition and Subtraction
Selected National Curriculum Programme of Study Statements
Pupils should be taught to:
add and subtract numbers with up to 4 digits using the formal written methods of columnar addition and subtraction where appropriate
solve addition and subtraction two-step problems in context, deciding which operations and methods to use and why
The Big Ideas
It helps to round numbers before carrying out a calculation to get a sense of the size of the answer. For example, 4786 – 2135 is close to 5000 – 2000, so the answer will
be around 3000. Looking at the numbers in a calculation and their relationship to each other can help make calculating easier. For example, 3012 – 2996. Noticing that
the numbers are close to each other might mean this is more easily calculated by thinking about subtraction as difference.
Mastery Check
Please note that the following columns provide indicative examples of the sorts of tasks and questions that provide evidence for mastery and mastery with greater
depth of the selected programme of study statements. Pupils may be able to carry out certain procedures and answer questions like the ones outlined, but the
teacher will need to check that pupils really understand the idea by asking questions such as ‘Why?’, ‘What happens if …?’, and checking that pupils can use the
procedures or skills to solve a variety of problems.
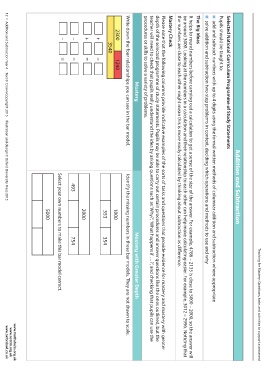
Mastery Mastery with Greater Depth
Write down the four relationships you can see in the bar model. Identify the missing numbers in these bar models. They are not drawn to scale.
2300 1240 1000
3540
353 354
+ =
+ =
2000
– = 493 754
– =
Select your own numbers to make this bar model correct.
5000
www.mathshubs.org.uk
www.ncetm.org.uk
12 • Addition and Subtraction Year 4 Text © Crown Copyright 2015 Illustration and design © Oxford University Press 2015 www.oxfordowl.co.uk