Page 91 - The national curriculum in England - Framework document
P. 91
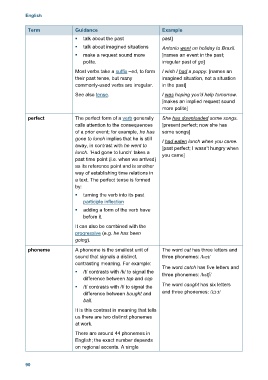
English
Term Guidance Example
talk about the past past]
talk about imagined situations Antonio went on holiday to Brazil.
make a request sound more [names an event in the past;
polite. irregular past of go]
Most verbs take a suffix –ed, to form I wish I had a puppy. [names an
their past tense, but many imagined situation, not a situation
commonly-used verbs are irregular. in the past]
See also tense. I was hoping you’d help tomorrow.
[makes an implied request sound
more polite]
perfect The perfect form of a verb generally She has downloaded some songs.
calls attention to the consequences [present perfect; now she has
of a prior event; for example, he has some songs]
gone to lunch implies that he is still I had eaten lunch when you came.
away, in contrast with he went to [past perfect; I wasn’t hungry when
lunch. ‘Had gone to lunch’ takes a you came]
past time point (i.e. when we arrived)
as its reference point and is another
way of establishing time relations in
a text. The perfect tense is formed
by:
turning the verb into its past
participle inflection
adding a form of the verb have
before it.
It can also be combined with the
progressive (e.g. he has been
going).
phoneme A phoneme is the smallest unit of The word cat has three letters and
sound that signals a distinct, three phonemes: /kæt/
contrasting meaning. For example:
The word catch has five letters and
/t/ contrasts with /k/ to signal the three phonemes: /kaʧ/
difference between tap and cap
/t/ contrasts with /l/ to signal the The word caught has six letters
difference between bought and and three phonemes: /kɔ:t/
ball.
It is this contrast in meaning that tells
us there are two distinct phonemes
at work.
There are around 44 phonemes in
English; the exact number depends
on regional accents. A single
90