Page 33 - Petzl-catalog-pro-2018
P. 33
General rescue principles
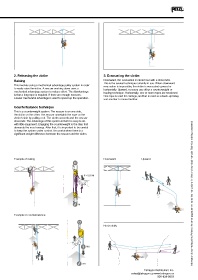
2. Releasing the victim 3. Evacuating the victim
Raising Downward, the evacuation is carried out with a descender.
This involves using a mechanical advantage pulley system in order This is the easiest technique currently in use. When downward
evacuation is impossible, the victim is evacuated upward or
to easily raise the victim. A rescuer working alone uses a horizontally. Upward, rescuers use either a counterweight or
mechanical advantage system to reduce effort. The disadvantage hauling technique. Horizontally, one or more ropes are tensioned.
is that a long rope is required. If there are enough rescuers, One rope is used for carriage, another is used as a back-up belay,
a lower mechanical advantage is used to speed up the operation. and another to move the litter.
Counterbalance technique
This is a counterweight system. The rescuer is on one side,
the victim on the other. The rescuer unweights the rope on the
victim's side by pulling on it. The victim ascends and the rescuer
descends. The advantage of this system is that it is easy to do
with little equipment. Engaging the counterweight is the step that
demands the most energy. After that, it is important to be careful
to keep the system under control. Be careful when there is a
significant weight difference between the rescuer and the victim.
Example of raising Downward Upward
F = 0,25 M
F = 0,25 M
M Information is non-exhaustive. Refer to the other pages as well as to the Instructions for Use and technical manuals. Technical training is essential.
M
Example of counterbalance
Horizontally
M2
M2
M1
M1
Tetragon Distributors Inc.
sales@tetragon.ca www.tetragon.ca
905-828-9803