Page 359 - COSO Guidance
P. 359
Thought Leadership in ERM | Risk Assessment in Practice | 17
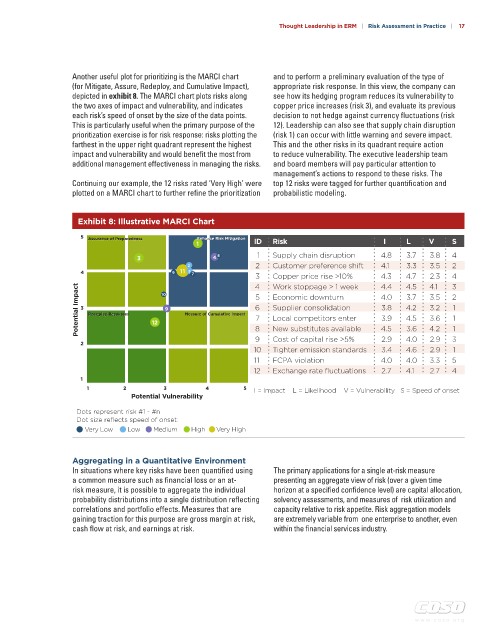
Another useful plot for prioritizing is the MARCI chart and to perform a preliminary evaluation of the type of
(for Mitigate, Assure, Redeploy, and Cumulative Impact), appropriate risk response. In this view, the company can
depicted in exhibit 8. The MARCI chart plots risks along see how its hedging program reduces its vulnerability to
the two axes of impact and vulnerability, and indicates copper price increases (risk 3), and evaluate its previous
each risk’s speed of onset by the size of the data points. decision to not hedge against currency fluctuations (risk
This is particularly useful when the primary purpose of the 12). Leadership can also see that supply chain disruption
prioritization exercise is for risk response: risks plotting the (risk 1) can occur with little warning and severe impact.
farthest in the upper right quadrant represent the highest This and the other risks in its quadrant require action
impact and vulnerability and would benefit the most from to reduce vulnerability. The executive leadership team
additional management effectiveness in managing the risks. and board members will pay particular attention to
management’s actions to respond to these risks. The
Continuing our example, the 12 risks rated ‘Very High’ were top 12 risks were tagged for further quantification and
plotted on a MARCI chart to further refine the prioritization probabilistic modeling.
Exhibit 8: Illustrative MARCI Chart
5 Assurance of Preparedness Enhance Risk Mitigation
Assurance of Preparedness
Enhance Risk Mitigation
1 ID Risk I L V S
3 4 8 1 Supply chain disruption 4.8 3.7 3.8 4
2 Customer preference shift 4.1 3.3 3.5 2
2
4 6 11 5 7 3 Copper price rise >10% 4.3 4.7 4.1 4
2.3
4
Work stoppage > 1 week
4.4
4.5
3
Potential Impact 3 Redeploy Resources 12 10 9 Measure of Cumulative Impact 5 Economic downturn 4.0 3.7 3.5 2
3.2
1
4.2
Supplier consolidation
6
3.8
Redeploy Resources
Measure of Cumulative Impact
Local competitors enter
1
3.6
7
4.5
3.9
1
2.9
Cost of capital rise >5%
2.9
9
4.0
2 8 New substitutes available 4.5 3.6 4.2 3
10 Tighter emission standards 3.4 4.6 2.9 1
11 FCPA violation 4.0 4.0 3.3 5
12 Exchange rate fluctuations 2.7 4.1 2.7 4
1
1 2 3 4 5 I = Impact L = Likelihood V = Vulnerability S = Speed of onset
Potential Vulnerability
Dots represent risk #1 - #n
Dot size reflects speed of onset:
Very Low Low Medium High Very High
Aggregating in a Quantitative Environment
In situations where key risks have been quantified using The primary applications for a single at-risk measure
a common measure such as financial loss or an at- presenting an aggregate view of risk (over a given time
risk measure, it is possible to aggregate the individual horizon at a specified confidence level) are capital allocation,
probability distributions into a single distribution reflecting solvency assessments, and measures of risk utilization and
correlations and portfolio effects. Measures that are capacity relative to risk appetite. Risk aggregation models
gaining traction for this purpose are gross margin at risk, are extremely variable from one enterprise to another, even
cash flow at risk, and earnings at risk. within the financial services industry.
w w w . c o s o . o r g