Page 105 - Zoo Animal Learning and Training
P. 105
Chapter 10: Transfrontal Craniotomy 103
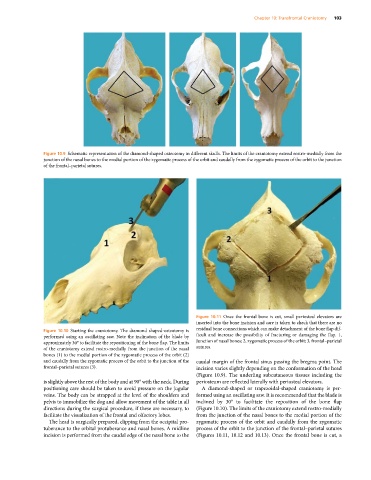
Figure 10.9 Schematic representation of the diamond‐shaped osteotomy in different skulls. The limits of the craniotomy extend rostro‐medially from the
junction of the nasal bones to the medial portion of the zygomatic process of the orbit and caudally from the zygomatic process of the orbit to the junction
of the frontal–parietal sutures.
Figure 10.11 Once the frontal bone is cut, small periosteal elevators are
inserted into the bone incision and care is taken to check that there are no
Figure 10.10 Starting the craniotomy. The diamond shaped‐osteotomy is residual bone connections which can make detachment of the bone flap dif
performed using an oscillating saw. Note the inclination of the blade by ficult and increase the possibility of fracturing or damaging the flap. 1,
approximately 30° to facilitate the repositioning of the bone flap. The limits Junction of nasal bones; 2, zygomatic process of the orbit; 3, frontal–parietal
of the craniotomy extend rostro‐medially from the junction of the nasal sutures.
bones (1) to the medial portion of the zygomatic process of the orbit (2)
and caudally from the zygomatic process of the orbit to the junction of the caudal margin of the frontal sinus passing the bregma point. The
frontal–parietal sutures (3). incision varies slightly depending on the conformation of the head
(Figure 10.9). The underling subcutaneous tissues including the
is slightly above the rest of the body and at 90° with the neck. During periosteum are reflected laterally with periosteal elevators.
positioning care should be taken to avoid pressure on the jugular A diamond‐shaped or trapezoidal‐shaped craniotomy is per
veins. The body can be strapped at the level of the shoulders and formed using an oscillating saw. It is recommended that the blade is
pelvis to immobilize the dog and allow movement of the table in all inclined by 30° to facilitate the reposition of the bone flap
directions during the surgical procedure, if these are necessary, to (Figure 10.10). The limits of the craniotomy extend rostro‐medially
facilitate the visualization of the frontal and olfactory lobes. from the junction of the nasal bones to the medial portion of the
The head is surgically prepared, clipping from the occipital pro zygomatic process of the orbit and caudally from the zygomatic
tuberance to the orbital protuberance and nasal bones. A midline process of the orbit to the junction of the frontal–parietal sutures
incision is performed from the caudal edge of the nasal bone to the (Figures 10.11, 10.12 and 10.13). Once the frontal bone is cut, a