Page 1239 - Equine Clinical Medicine, Surgery and Reproduction, 2nd Edition
P. 1239
1214 CHAPTER 12
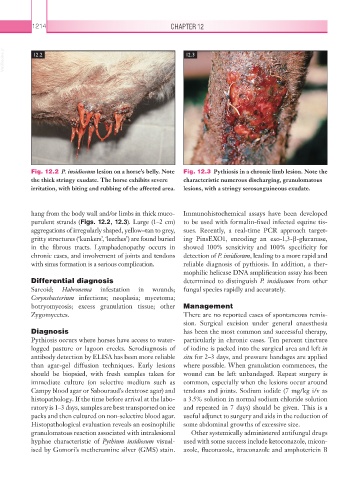
VetBooks.ir 12.2 12.3
Fig. 12.2 P. insidiosum lesion on a horse’s belly. Note Fig. 12.3 Pythiosis in a chronic limb lesion. Note the
the thick stringy exudate. The horse exhibits severe characteristic numerous discharging, granulomatous
irritation, with biting and rubbing of the affected area. lesions, with a stringy serosanguineous exudate.
hang from the body wall and/or limbs in thick muco- Immunohistochemical assays have been developed
purulent strands (Figs. 12.2, 12.3). Large (1–2 cm) to be used with formalin-fixed infected equine tis-
aggregations of irregularly shaped, yellow–tan to grey, sues. Recently, a real-time PCR approach target-
gritty structures (‘kunkers’, ‘leeches’) are found buried ing PinsEXO1, encoding an exo-1,3-β-glucanase,
in the fibrous tracts. Lymphadenopathy occurs in showed 100% sensitivity and 100% specificity for
chronic cases, and involvement of joints and tendons detection of P. insidiosum, leading to a more rapid and
with sinus formation is a serious complication. reliable diagnosis of pythiosis. In addition, a ther-
mophilic helicase DNA amplification assay has been
Differential diagnosis determined to distinguish P. insidiosum from other
Sarcoid; Habronema infestation in wounds; fungal species rapidly and accurately.
Corynebacterium infections; neoplasia; mycetoma;
botryomycosis; excess granulation tissue; other Management
Zygomycetes. There are no reported cases of spontaneous remis-
sion. Surgical excision under general anaesthesia
Diagnosis has been the most common and successful therapy,
Pythiosis occurs where horses have access to water- particularly in chronic cases. Ten percent tincture
logged pasture or lagoon creeks. Serodiagnosis of of iodine is packed into the surgical area and left in
antibody detection by ELISA has been more reliable situ for 2–3 days, and pressure bandages are applied
than agar-gel diffusion techniques. Early lesions where possible. When granulation commences, the
should be biopsied, with fresh samples taken for wound can be left unbandaged. Repeat surgery is
immediate culture (on selective medium such as common, especially when the lesions occur around
Campy blood agar or Sabouraud’s dextrose agar) and tendons and joints. Sodium iodide (7 mg/kg i/v as
histopathology. If the time before arrival at the labo- a 3.5% solution in normal sodium chloride solution
ratory is 1–3 days, samples are best transported on ice and repeated in 7 days) should be given. This is a
packs and then cultured on non-selective blood agar. useful adjunct to surgery and aids in the reduction of
Histopathological evaluation reveals an eosinophilic some abdominal growths of excessive size.
granulomatous reaction associated with intralesional Other systemically administered antifungal drugs
hyphae characteristic of Pythium insidiosum visual- used with some success include ketoconazole, micon-
ised by Gomori’s methenamine silver (GMS) stain. azole, fluconazole, itraconazole and amphotericin B