Page 1188 - Adams and Stashak's Lameness in Horses, 7th Edition
P. 1188
1154 Chapter 12
VetBooks.ir
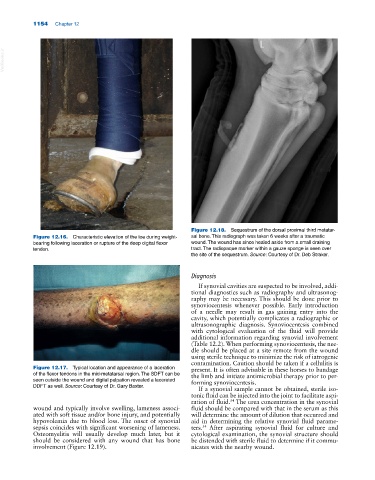
Figure 12.18. Sequestrum of the dorsal proximal third metatar-
Figure 12.16. Characteristic elevation of the toe during weight‐ sal bone. This radiograph was taken 6 weeks after a traumatic
bearing following laceration or rupture of the deep digital flexor wound. The wound has since healed aside from a small draining
tendon. tract. The radiopaque marker within a gauze sponge is seen over
the site of the sequestrum. Source: Courtesy of Dr. Deb Straker.
Diagnosis
If synovial cavities are suspected to be involved, addi
tional diagnostics such as radiography and ultrasonog
raphy may be necessary. This should be done prior to
synoviocentesis whenever possible. Early introduction
of a needle may result in gas gaining entry into the
cavity, which potentially complicates a radiographic or
ultrasonographic diagnosis. Synoviocentesis combined
with cytological evaluation of the fluid will provide
additional information regarding synovial involvement
(Table 12.2). When performing synoviocentesis, the nee
dle should be placed at a site remote from the wound
using sterile technique to minimize the risk of iatrogenic
contamination. Caution should be taken if a cellulitis is
Figure 12.17. Typical location and appearance of a laceration present. It is often advisable in these horses to bandage
of the flexor tendons in the mid‐metatarsal region. The SDFT can be the limb and initiate antimicrobial therapy prior to per
seen outside the wound and digital palpation revealed a lacerated forming synoviocentesis.
DDFT as well. Source: Courtesy of Dr. Gary Baxter.
If a synovial sample cannot be obtained, sterile iso
tonic fluid can be injected into the joint to facilitate aspi
ration of fluid. The urea concentration in the synovial
54
wound and typically involve swelling, lameness associ fluid should be compared with that in the serum as this
ated with soft tissue and/or bone injury, and potentially will determine the amount of dilution that occurred and
hypovolemia due to blood loss. The onset of synovial aid in determining the relative synovial fluid parame
sepsis coincides with significant worsening of lameness. ters. After aspirating synovial fluid for culture and
54
Osteomyelitis will usually develop much later, but it cytological examination, the synovial structure should
should be considered with any wound that has bone be distended with sterile fluid to determine if it commu
involvement (Figure 12.19). nicates with the nearby wound.