Page 470 - Feline diagnostic imaging
P. 470
482 27 Urinary Disease
fibrinohemorrhagic tissue adhering to a thickened 27.4.4 Neoplasia
bladder wall. The urine contained a fibrinous exudate, The most common neoplasm in the urinary bladder is tran-
blood clots, necrotic and suppurative material, and focal
mineralization. The sonographic appearance was simi- sitional cell carcinoma (Figure 27.33) but other neoplasms
occur, such as lymphosarcoma (Figure 27.34) [41].
lar in the four cats: the bladder had a thickened wall and
appeared compartmentalized because of septae crossing Transitional cell carcinoma is less likely to be at the trigone
in cats than in dogs. In one study, 55% of 20 neoplasms had
the lumen. Bladder contents were echogenic. Double
contrast cystography in one cat revealed a thickened a location other than the trigone [42]. In another, only 3/11
cats had transitional cell carcinoma at the trigone [43].
bladder wall and a lumen contained a large amount of
solid material. Neoplasia is rarely detectable on survey radiography.
Bladder masses are painful, resulting in frequent urination
Severe cystitis and polyploid cystitis can resemble neopla-
sia. Traumatic catheterization or endoscopy can be used to and a normal‐sized bladder. Rarely, mineralization in the
bladder wall may signal the presence of neoplasia.
help differentiate these conditions. Most, but not all, polyps
are associated with transitional cell carcinoma. Blood clots Additionally, there may be evidence of metastasis to other
organs including lymph nodes, lungs, and bone.
can be mistaken for masses within the bladder. Repositioning
Double contrast cystography is the preferred contrast pro-
the patient can help show that a clot is not associated with cedure for evaluation of suspected neoplasia. The mass
the bladder wall but some blood clots adhere to the bladder
wall and are more difficult to differentiate. Those free in the shows as a filling defect when it is on the dependent side but
it will be coated with contrast on the nondependent side.
lumen can be mistaken for calculi. When hemorrhage is
present in the bladder, the bladder should be gently flushed The neoplasm usually presents as a polyploid mass but in
some cases, there is severe mural thickening. Hydronephrosis
with saline to help remove blood clots.
(a) (b)
(c)
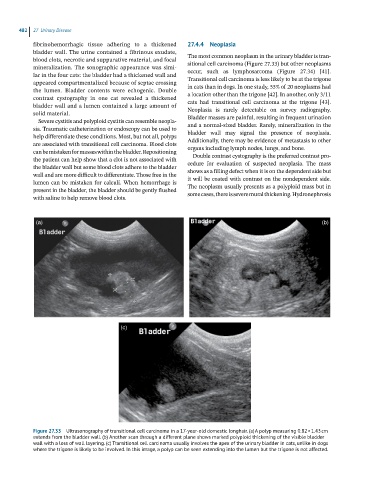
Figure 27.33 Ultrasonography of transitional cell carcinoma in a 17-year-old domestic longhair. (a) A polyp measuring 0.82 × 1.43 cm
extends from the bladder wall. (b) Another scan through a different plane shows marked polyploid thickening of the visible bladder
wall with a loss of wall layering. (c) Transitional cell carcinoma usually involves the apex of the urinary bladder in cats, unlike in dogs
where the trigone is likely to be involved. In this image, a polyp can be seen extending into the lumen but the trigone is not affected.