Page 1304 - Cote clinical veterinary advisor dogs and cats 4th
P. 1304
Mitral Valve Dysplasia 657
Mitral Valve Dysplasia Client Education
Sheet
VetBooks.ir Diseases and Disorders
BASIC INFORMATION
Pathophysiology
• Mitral regurgitation • Electrocardiogram (ECG): wide P waves in
lead II, supraventricular premature com-
Definition • Obstruction of the transmitral diastolic flow plexes, atrial/supraventricular tachycardia,
Congenital malformation of any component of (increase in resistance to blood flow between atrial fibrillation. Increased R-wave amplitude
the mitral valve apparatus (papillary muscles, the left atrium and ventricle) in MVS in lead II
chordae tendineae, leaflets, annulus) that results • Obstruction of the left ventricular outflow • Echocardiogram
in valvular dysfunction tract with SAM ○ Two- (and three-) dimensional mode:
• Increase in left atrial, pulmonary venous, abnormal mitral valve leaflets, abnormal
Epidemiology and pulmonary capillary pressures valve motion, mitral regurgitation, left
SPECIES, AGE, SEX • Pulmonary edema formation atrial dilation. Supravalvular membrane
Dogs and cats; usually identified early in life • Exercise increases left atrial pressure; exercise- (cat), decreased mitral valve leaflet excur-
induced dyspnea/syncope may occur. sion, and diastolic doming of the leaflets
GENETICS, BREED PREDISPOSITION • PH can develop secondary to increased (MVS)
• Dogs: bull terrier, miniature bull terrier, pulmonary capillary pressure. ○ M-mode: thickened mitral valve leaflets,
English bulldog, Great Dane, German increased left atrial/aortic (LA/Ao) ratio,
shepherd, Newfoundland, and Irish setter DIAGNOSIS incomplete leaflet separation in diastole
are predisposed. and reduced mid-diastolic closure velocity
• Cats: male Siamese cats are overrepresented Diagnostic Overview (E-F slope) (MVS); SAM
(valvular and supravalvular stenosis). The diagnosis is suspected in a young patient ○ Color-flow Doppler: systolic turbulent flow
presenting with a left apical systolic heart in the left atrium with mitral regurgitation
RISK FACTORS murmur that may have cough, tachypnea, and in the left ventricular outflow tract
Predisposed breeds of dogs and dyspnea. Left heart enlargement is with SAM. Diastolic aliased or turbulent
usually evident on thoracic radiographs, and flow across the mitral valve (MVS)
ASSOCIATED DISORDERS an echocardiogram is required for confirmation. ○ Spectral Doppler: increased early diastolic
• Dogs (concurrent conditions) filling (velocity of E wave > 1.1 m/s),
○ Systolic anterior motion (SAM) of the Differential Diagnosis prolonged pressure half-time (>50 ms),
mitral valve • Radiographic/electrocardiographic and reduced mitral valve area (MVS)
○ Subaortic stenosis (SAS) ○ Left atrial enlargement: other types of
○ Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) cardiac disease (myxomatous mitral Advanced or Confirmatory Testing
○ Pulmonic stenosis valve disease/endocardiosis, dilated car- • Cardiac catheterization: rarely necessary for
• Dogs and cats (associated conditions) diomyopathy, SAS, PDA, and [in cats] confirming diagnosis but may yield quan-
○ Congestive heart failure (CHF) hypertrophic cardiomyopathy) titative information and help characterize
○ Pulmonary hypertension (PH) • Echocardiographic unusual lesions
• Cats (concurrent and associated condition): ○ Myxomatous mitral valve disease/ ○ Angiogram: mitral regurgitation, thickened
feline aortic thromboembolism endocardiosis and/or restricted mitral valve leaflets,
○ Bacterial endocarditis enlarged left atrium
Clinical Presentation ○ Intracardiac neoplasia ○ Pressure measurements: increase in left
DISEASE FORMS/SUBTYPES atrial pressure and pulmonary artery
• Mitral valve stenosis (MVS) involves the Initial Database pressure with PH or CHF
mitral valve leaflets (dog and cat). • Thoracic radiographs: left atrial enlargement • Transesophageal echocardiography: better
• Supravalvular mitral stenosis very common; signs of pulmonary edema if visualization of the mitral valve apparatus
CHF but requires general anesthesia
HISTORY, CHIEF COMPLAINT
• Exercise intolerance/episodic weakness
• Lethargy
• Cough
• Dyspnea (most common sign in cats)
• Syncope
PHYSICAL EXAM FINDINGS
• Left apical systolic murmur (if mitral
regurgitation)
• Soft left apical diastolic murmur (MVS)
• With CHF
○ Tachycardia
○ Tachypnea B
○ Pulmonary crackles and wheezes A
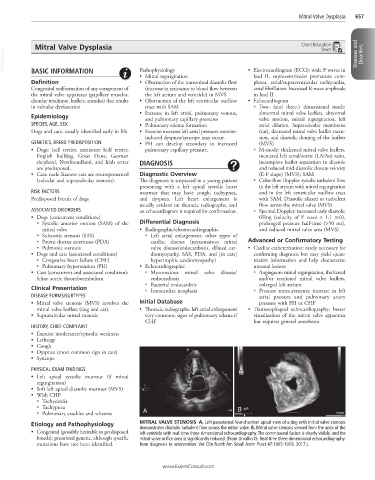
Etiology and Pathophysiology MITRAL VALVE STENOSIS A, Left parasternal four-chamber apical view of a dog with mitral valve stenosis
• Congenital (possibly heritable in predisposed demonstrates diastolic turbulent flow across the mitral valve. B, Mitral valve stenosis viewed from the apex of the
left ventricle with real-time three-dimensional echocardiography. The commissural fusion is clearly visible, and the
breeds); presumed genetic, although specific mitral valve orifice area is significantly reduced. (From Orvalho JS: Real-time three-dimensional echocardiography:
mutations have not been identified. from diagnosis to intervention. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract 47:1005-1019, 2017.).
www.ExpertConsult.com