Page 1762 - Cote clinical veterinary advisor dogs and cats 4th
P. 1762
886 Retinal Detachment
VetBooks.ir
A B
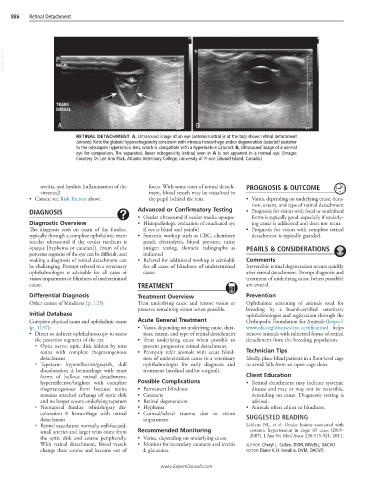
RETINAL DETACHMENT A, Ultrasound image of an eye (anterior/rostral is at the top) shows retinal detachment
(arrows). Note the globoid hyperechogenicity consistent with vitreous hemorrhage and/or degeneration (asterisk) posterior
to the misshapen hyperechoic lens, which is compatible with a hypermature cataract. B, Ultrasound image of a normal
eye for comparison. The separated, linear echogenicity (retina) seen in A is not apparent in a normal eye. (Images
Courtesy Dr. Lee Ann Pack, Atlantic Veterinary College, University of Prince Edward Island, Canada.)
uveitis, and hyalitis [inflammation of the focus. With some cases of retinal detach- PROGNOSIS & OUTCOME
vitreous]) ment, blood vessels may be visualized in
• Causes: see Risk Factors above. the pupil behind the lens. • Varies, depending on underlying cause, dura-
tion, extent, and type of retinal detachment
DIAGNOSIS Advanced or Confirmatory Testing • Prognosis for vision with focal or multifocal
• Ocular ultrasound if ocular media opaque forms is typically good, especially if underly-
Diagnostic Overview • Histopathologic evaluation of enucleated eye ing cause is addressed and does not recur.
The diagnosis rests on exam of the fundus, if eye is blind and painful • Prognosis for vision with complete retinal
typically through a complete ophthalmic exam • Systemic workup such as CBC, chemistry detachment is typically guarded.
(ocular ultrasound if the ocular medium is panel, electrolytes, blood pressure, urine
opaque [hyphema or cataract]). Exam of the antigen testing, thoracic radiographs as PEARLS & CONSIDERATIONS
posterior segment of the eye can be difficult, and indicated
making a diagnosis of retinal detachment can • Referral for additional workup is advisable Comments
be challenging. Prompt referral to a veterinary for all cases of blindness of undetermined Irreversible retinal degeneration occurs quickly
ophthalmologist is advisable for all cases of cause. after retinal detachment. Prompt diagnosis and
vision impairment or blindness of undetermined treatment of underlying cause (when possible)
cause. TREATMENT are crucial.
Differential Diagnosis Treatment Overview Prevention
Other causes of blindness (p. 123) Treat underlying cause and restore vision or Ophthalmic screening of animals used for
preserve remaining vision when possible. breeding by a board-certified veterinary
Initial Database ophthalmologist and registration through the
Complete physical exam and ophthalmic exam Acute General Treatment Orthopedic Foundation for Animals (https://
(p. 1137): • Varies, depending on underlying cause, dura- www.ofa.org/diseases/eye-certification) helps
• Direct or indirect ophthalmoscopy to assess tion, extent, and type of retinal detachment remove animals with inherited forms of retinal
the posterior segment of the eye • Treat underlying cause when possible to detachment from the breeding population.
○ Optic nerve: optic disk hidden by torn prevent progressive retinal detachment.
retina with complete rhegmatogenous • Promptly refer animals with acute blind- Technician Tips
detachment ness of undetermined cause to a veterinary Ideally, place blind patients in a floor-level cage
○ Tapetum: hyporeflective/grayish, dull ophthalmologist for early diagnosis and to avoid falls from an open cage door.
discoloration ± hemorrhage with most treatment (medical and/or surgical).
forms of bullous retinal detachment; Client Education
hyperreflective/brighter with complete Possible Complications • Retinal detachment may indicate systemic
rhegmatogenous form because retina • Permanent blindness disease and may or may not be reversible,
remains attached at/hangs off optic disk • Cataracts depending on cause. Diagnostic testing is
and no longer covers underlying tapetum • Retinal degeneration advised.
○ Nontapetal fundus: whitish/gray dis- • Hyphema • Animals often adjust to blindness.
coloration ± hemorrhage with retinal • Corneal/scleral trauma due to vision
detachment impairment SUGGESTED READING
○ Retinal vasculature: normally, well-focused, Leblanc NL, et al: Ocular lesions associated with
small arteries and larger veins come from Recommended Monitoring systemic hypertension in dogs: 65 cases (2005-
the optic disk and course peripherally. • Varies, depending on underlying cause 2007). J Am Vet Med Assoc 238:915-921, 2011.
With retinal detachment, blood vessels • Monitor for secondary cataracts and uveitis AUTHOR: Cheryl L. Cullen, DVM, MVetSc, DACVO
change their course and become out of ± glaucoma. EDITOR: Diane V. H. Hendrix, DVM, DACVO
www.ExpertConsult.com