Page 275 - Cote clinical veterinary advisor dogs and cats 4th
P. 275
Bilious Vomiting Syndrome 119
○ Choledochotomy: for removal of stones Common
that are lodged in the common bile duct bile duct Gallbladder
VetBooks.ir ○ Bile duct resection and anastomosis: for Cystic duct Diseases and Disorders
High risk of dehiscence
■
Hepatic ducts
stricture or damage/trauma – only if bile
duct is distended
papilla
High risk of dehiscence Major duodenal
■
○ Gastrointestinal biopsies: association of Duodenum Minor pancreatic duct
biliary disease with inflammatory bowel
disease and possibly eosinophilic sclerosing Minor duodenal Major pancreatic duct
fibroplasia in cats papilla
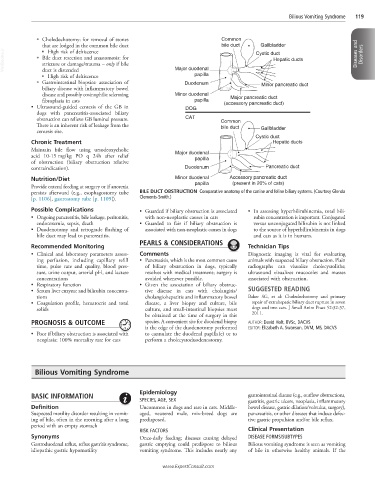
• Ultrasound-guided centesis of the GB in DOG (accessory pancreatic duct)
dogs with pancreatitis-associated biliary
obstruction can relieve GB luminal pressure. CAT Common
There is an inherent risk of leakage from the bile duct Gallbladder
centesis site.
Cystic duct
Chronic Treatment Hepatic ducts
Maintain bile flow using ursodeoxycholic Major duodenal
acid 10-15 mg/kg PO q 24h after relief papilla
of obstruction (biliary obstruction relative
contraindication). Duodenum Pancreatic duct
Nutrition/Diet Minor duodenal Accessory pancreatic duct
Provide enteral feeding at surgery or if anorexia papilla (present in 20% of cats)
persists afterward (e.g., esophagostomy tube BILE DUCT OBSTRUCTION Comparative anatomy of the canine and feline biliary systems. (Courtesy Glenda
[p. 1106], gastrostomy tube [p. 1109]). Clements-Smith.)
Possible Complications • Guarded if biliary obstruction is associated • In assessing hyperbilirubinemia, total bili-
• Ongoing pancreatitis, bile leakage, peritonitis, with non-neoplastic causes in cats rubin concentration is important. Conjugated
endotoxemia, sepsis, death • Guarded to fair if biliary obstruction is versus unconjugated bilirubin is not linked
• Duodenotomy and retrograde flushing of associated with non-neoplastic causes in dogs to the source of hyperbilirubinemia in dogs
bile duct may lead to pancreatitis. and cats as it is in humans.
PEARLS & CONSIDERATIONS
Recommended Monitoring Technician Tips
• Clinical and laboratory parameters assess- Comments Diagnostic imaging is vital for evaluating
ing perfusion, including capillary refill • Pancreatitis, which is the most common cause animals with suspected biliary obstruction. Plain
time, pulse rate and quality, blood pres- of biliary obstruction in dogs, typically radiographs can visualize cholecystoliths;
sure, urine output, arterial pH, and lactate resolves with medical treatment; surgery is ultrasound visualizes mucoceles and masses
concentrations avoided whenever possible. associated with obstruction.
• Respiratory function • Given the association of biliary obstruc-
• Serum liver enzyme and bilirubin concentra- tive disease in cats with cholangitis/ SUGGESTED READING
tions cholangiohepatitis and inflammatory bowel Baker SG, et al: Choledochotomy and primary
• Coagulation profile, hematocrit and total disease, a liver biopsy and culture, bile repair of extrahepatic biliary duct rupture in seven
solids culture, and small-intestinal biopsies must dogs and two cats. J Small Anim Pract 52:32-37,
be obtained at the time of surgery in this 2011.
PROGNOSIS & OUTCOME species. A convenient site for duodenal biopsy AUTHOR: David Holt, BVSc, DACVS
is the edge of the duodenotomy performed EDITOR: Elizabeth A. Swanson, DVM, MS, DACVS
• Poor if biliary obstruction is associated with to cannulate the duodenal papilla(e) or to
neoplasia: 100% mortality rate for cats perform a cholecystoduodenostomy.
Bilious Vomiting Syndrome
Epidemiology
BASIC INFORMATION gastrointestinal disease (e.g., outflow obstructions,
SPECIES, AGE, SEX gastritis, gastric ulcers, neoplasia, inflammatory
Definition Uncommon in dogs and rare in cats. Middle- bowel disease, gastric dilation/volvulus, surgery),
Suspected motility disorder resulting in vomit- aged, neutered male, mix-breed dogs are pancreatitis, or other diseases that induce defec-
ing of bile, often in the morning after a long predisposed. tive gastric propulsion and/or bile reflux.
period with an empty stomach
RISK FACTORS Clinical Presentation
Synonyms Once-daily feeding; diseases causing delayed DISEASE FORMS/SUBTYPES
Gastroduodenal reflux, reflux gastritis syndrome, gastric emptying could predispose to bilious Bilious vomiting syndrome is seen as vomiting
idiopathic gastric hypomotility vomiting syndrome. This includes nearly any of bile in otherwise healthy animals. If the
www.ExpertConsult.com