Page 535 - Cote clinical veterinary advisor dogs and cats 4th
P. 535
Deciduous Teeth, Persistent (Retained) 239
nonsteroidal antiinflammatory medication
(e.g., carprofen 2 mg/kg PO q 12h) for 2-3
VetBooks.ir * * Possible Complications Diseases and Disorders
days postoperatively.
• Root fracture and retained root tips, leading
to infection of the permanent tooth
• Retarded eruption, malpositioning, and/or
mechanical damage to the permanent tooth
• Accidental extraction of permanent tooth
* * Recommended Monitoring
• Examination in 1-2 weeks to evaluate extrac-
tion sites
• Examination in 4-6 weeks to evaluate occlu-
sion if necessary; if abnormalities persist,
therapeutic recommendations are offered.
A B PROGNOSIS & OUTCOME
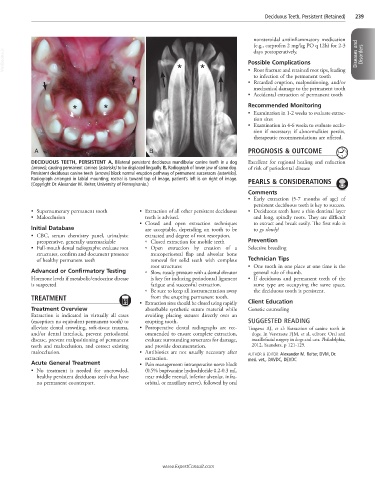
DECIDUOUS TEETH, PERSISTENT A, Bilateral persistent deciduous mandibular canine teeth in a dog Excellent for regional healing and reduction
(arrows), causing permanent canines (asterisks) to be displaced lingually. B, Radiograph of lower jaw of same dog. of risk of periodontal disease
Persistent deciduous canine teeth (arrows) block normal eruption pathway of permanent successors (asterisks).
Radiograph arranged in labial mounting; rostral is toward top of image, patient’s left is on right of image. PEARLS & CONSIDERATIONS
(Copyright Dr. Alexander M. Reiter, University of Pennsylvania.)
Comments
• Early extraction (5-7 months of age) of
persistent deciduous teeth is key to success.
• Supernumerary permanent tooth • Extraction of all other persistent deciduous • Deciduous teeth have a thin dentinal layer
• Malocclusion teeth is advised. and long, spindly roots. They are difficult
• Closed and open extraction techniques to extract and break easily. The first rule is
Initial Database are acceptable, depending on tooth to be to go slowly!
• CBC, serum chemistry panel, urinalysis: extracted and degree of root resorption.
preoperative, generally unremarkable ○ Closed extraction for mobile teeth Prevention
• Full-mouth dental radiographs: evaluate root ○ Open extraction by creation of a Selective breeding
structures, confirm and document presence mucoperiosteal flap and alveolar bone
of healthy permanent teeth removal for solid teeth with complete Technician Tips
root structures • One tooth in one place at one time is the
Advanced or Confirmatory Testing ○ Slow, steady pressure with a dental elevator general rule of thumb.
Hormone levels if metabolic/endocrine disease is key for inducing periodontal ligament • If deciduous and permanent teeth of the
is suspected fatigue and successful extraction. same type are occupying the same space,
○ Be sure to keep all instrumentation away the deciduous tooth is persistent.
TREATMENT from the erupting permanent tooth.
• Extraction sites should be closed using rapidly Client Education
Treatment Overview absorbable synthetic suture material while Genetic counseling
Extraction is indicated in virtually all cases avoiding placing sutures directly over an
(exception: no equivalent permanent tooth) to erupting tooth. SUGGESTED READING
alleviate dental crowding, soft-tissue trauma, • Postoperative dental radiographs are rec- Tsugawa AJ, et al: Extraction of canine teeth in
and/or dental interlock, prevent periodontal ommended to ensure complete extraction, dogs. In Verstraete FJM, et al, editors: Oral and
disease, prevent malpositioning of permanent evaluate surrounding structures for damage, maxillofacial surgery in dogs and cats. Philadelphia,
teeth and malocclusion, and correct existing and provide documentation. 2012, Saunders, p 121-129.
malocclusion. • Antibiotics are not usually necessary after AUTHOR & EDITOR: Alexander M. Reiter, DVM, Dr.
extraction. med. vet., DAVDC, DEVDC
Acute General Treatment • Pain management: intraoperative nerve block
• No treatment is needed for uncrowded, (0.5% bupivacaine hydrochloride 0.2-0.3 mL
healthy persistent deciduous teeth that have near middle mental, inferior alveolar, infra-
no permanent counterpart. orbital, or maxillary nerve), followed by oral
www.ExpertConsult.com