Page 895 - Cote clinical veterinary advisor dogs and cats 4th
P. 895
434 Hemorrhage
generally a more specific and reproduc- ACT, aPTT, PT, and TCT are pro- TREATMENT
ible test than the ACT. ■ Hemorrhagic DIC typically results in Treatment Overview
longed, and fibrinogen is low.
VetBooks.ir coagulopathies such as hemophilia and depletion of all factors and fibrinogen. The two main goals are to control bleeding
Long aPTT is seen in hereditary
■
in combined factor deficiencies such as
Mild to severe prolongation of clot-
and stabilize the patient with one or more of
rodenticide intoxication and DIC.
Prolongation of aPTT to a target ting times and low fibrinogen levels the following: local wound care, supportive
medical therapy, and/or transfusion therapy.
accompany hemorrhagic DIC. In
■
value of 1.5-2 times baseline is used contrast, high fibrinogen level may It is important to collect pretreatment samples
for adjusting unfractionated heparin accompany thrombotic DIC and other to perform screening and confirmatory tests.
dosage. hypercoagulable syndromes. Additional information on treatment is available
Hemorrhage caused by blood vessel Hemorrhage due to anticoagulant drug on p. 57.
■ ■
defects or primary hemostatic defects overdose or envenomation causes factor
(platelet abnormalities) should not inhibition or fibrinogen depletion. All Acute General Treatment
produce abnormal aPTT results. coagulation screening tests can detect • Hemorrhagic/hypovolemic shock: volume
○ Prothrombin time (PT [p. 1377]) severe drug overdose; however, aPTT replacement (intravenous fluid therapy [p.
Test is sensitive to deficiencies of and PT are preferentially sensitive to 911]), red cell replacement (p. 1169).
■
extrinsic and common pathway factors. unfractionated heparin and warfarin • Blood vessel injuries: control bleeding after
Specific prolongation of PT is an levels, respectively. visualization of the damaged vessels (physical
■
indication of factor VII deficiency. exam, endoscopic exam, ultrasound exam,
Because factor VII is vitamin K depen- Advanced or Confirmatory Testing or surgical exploration).
dent with short plasma half-life (3-6 Based on results of initial database: • Bleeding diatheses: identify and correct
hours), prolongation of PT develops in • Thrombocytopenia: rule out collection/ the underlying cause of acquired bleeding
conditions causing vitamin K deficiency laboratory artifact; may include bone marrow, diatheses; transfusion if needed to correct
(e.g., anticoagulant rodenticide, severe spleen, and lymph node aspiration and cyto- hereditary defects or pending response to
hepatopathy). logic review; serologic evaluation to detect medical management
The anticoagulant effect of warfarin evidence of pathogens; platelet-associated
■
and its dosage adjustments are based on antibody testing Chronic Treatment
prolongation of PT and its calculated • Evaluation for platelet dysfunction Depends on underlying cause of hemorrhage
derivative, the international normalized • Thromboelastography (TEG)
ratio (INR). • Ancillary diagnostics to differentiate coagu- Drug Interactions
PIVKA (proteins induced by vitamin lopathies include specific coagulation factor Avoid drugs with anticoagulant or antiplatelet
■
K absence or antagonism) testing analyses, determinations of antithrombin effects (e.g., nonsteroidal antiinflammatory
performed using the Thrombotest assay activity and fibrin breakdown products, drugs, clopidogrel, sulfonamides, heparin,
and provides information equivalent to and drug detection (i.e., heparin or warfarin warfarin, plasma expanders, estrogens, cytotoxic
the PT. levels). drugs).
The PT is usually normal with hemor-
■
rhage caused by blood vessel defects
or primary hemostatic defects (platelet
abnormalities).
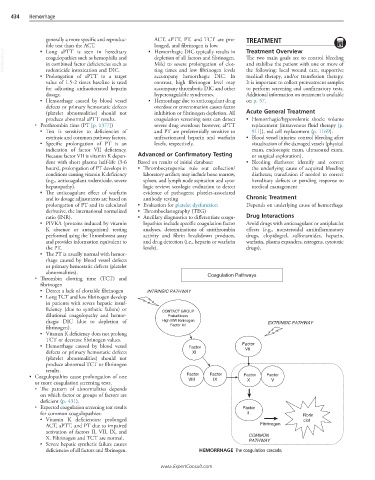
○ Thrombin clotting time (TCT) and Coagulation Pathways
fibrinogen
Detect a lack of clottable fibrinogen
■ INTRINSIC PATHWAY
Long TCT and low fibrinogen develop
■
in patients with severe hepatic insuf-
ficiency (due to synthetic failure) or CONTACT GROUP
dilutional coagulopathy and hemor- Prekallikrein
rhagic DIC (due to depletion of High MW Kininogen EXTRINSIC PATHWAY
fibrinogen). Factor XII
Vitamin K deficiency does not prolong
■
TCT or decrease fibrinogen values.
Hemorrhage caused by blood vessel Factor
■ Factor
defects or primary hemostatic defects XI VII
(platelet abnormalities) should not
produce abnormal TCT or fibrinogen
results.
• Coagulopathies cause prolongation of one Factor Factor Factor Factor
IX
VIII
or more coagulation screening tests. X V
○ The pattern of abnormalities depends
on which factor or groups of factors are
deficient (p. 431).
○ Expected coagulation screening test results Factor
for common coagulopathies: II Fibrin
Vitamin K deficiencies: prolonged
■ clot
ACT, aPTT, and PT due to impaired Fibrinogen
activation of factors II, VII, IX, and
X. Fibrinogen and TCT are normal. COMMON
Severe hepatic synthetic failure causes PATHWAY
■
deficiencies of all factors and fibrinogen. HEMORRHAGE The coagulation cascade.
www.ExpertConsult.com