Page 21 - A Practical Guide to Equine Radiography
P. 21
2 A PRACTICAL GUIDE TO EQUINE RADIOGRAPHY
produced, which are accelerated by apply- How do X-rays interact with matter?
VetBooks.ir ing a current to the system until they hit the • When X-rays hit matter, they can either pen-
positive anode at high speed.
etrate the material or get absorbed by it. The
• The higher the temperature of the cathode,
the more electrons are produced; this is main underlying principles on an atomic
level are called the Compton and the pho-
related to the mAs (milliampere seconds) toelectric effect. The Compton effect is less
settings of the X-ray machine. desirable since it is responsible for scatter
• The higher the speed of the electrons, the radiation that degrades image quality.
higher the penetrating power of the resulting • The degree of absorption of the X-rays by
X-rays. This is controlled by the kVp settings material is determined by the thickness and
of the X-ray machine. the radiodensity of the absorber.
• X-rays radiate from the source in straight • The radiodensity depends on the physical
lines in all directions. For medical purposes, density and the atomic number of the mate-
only a small cone of the X-rays, the primary rial, e.g. lead has a very high atomic number
beam, is used. which allows complete absorption of X-rays
• The size of the primary beam is set by adjust- with only a few millimetres of material. This
ing the window through which X-rays can is the reason why, for example, lead is used
leave the housing of the X-ray generator. for shielding purposes, e.g. in protective
This is called collimation and is an essential clothing. The same effect can be achieved
radiation protection mechanism, but also with material of lower atomic number by
optimizes image quality by reducing scatter. increasing its thickness, e.g. a 20 cm brick
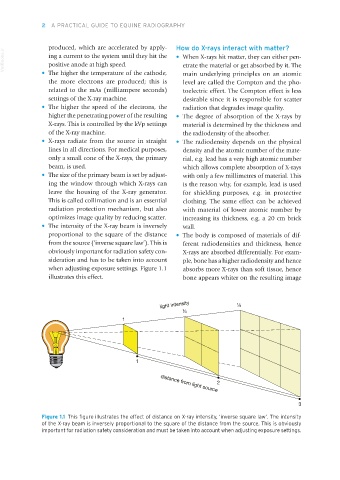
• The intensity of the X-ray beam is inversely wall.
proportional to the square of the distance • The body is composed of materials of dif-
from the source (‘inverse square law’). This is ferent radiodensities and thickness, hence
obviously important for radiation safety con- X-rays are absorbed differentially. For exam-
sideration and has to be taken into account ple, bone has a higher radiodensity and hence
when adjusting exposure settings. Figure 1.1 absorbs more X-rays than soft tissue, hence
illustrates this effect. bone appears whiter on the resulting image
light intensity 9
1
1
2
distance from light source
3
Figure 1.1 This figure illustrates the effect of distance on X-ray intensity, ‘inverse square law’. The intensity
of the X-ray beam is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the source. This is obviously
important for radiation safety consideration and must be taken into account when adjusting exposure settings.
Equine Radiography.indb 2 27/11/2018 11:03