Page 1412 - Small Animal Internal Medicine, 6th Edition
P. 1412
1384 PART XIII Hematology
HYPOCELLULAR
VetBooks.ir Normal cells Abnormal
cells
Increased Normal Neoplasia Dysplasia
reticulin reticulin
HL
Myelofibrosis Normal Toxic
cellularity Hypoplasia neoplasia
Metastatic
Disorders Estrogen Non- neoplasia Viral
in release estrogen
E. canis Iatrogenic E. canis MDS
SCT
Drug-related
Hyperestrogenism
Immune-mediated
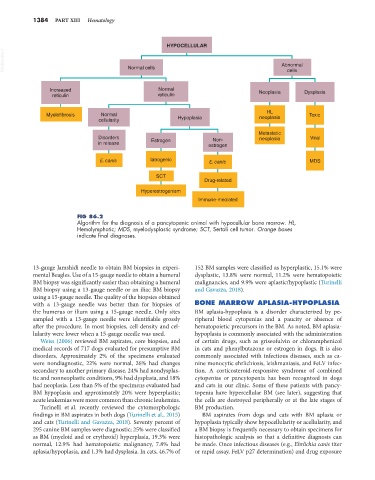
FIG 86.2
Algorithm for the diagnosis of a pancytopenic animal with hypocellular bone marrow. HL,
Hemolymphatic; MDS, myelodysplastic syndrome; SCT, Sertoli cell tumor. Orange boxes
indicate final diagnoses.
13-gauge Jamshidi needle to obtain BM biopsies in experi- 152 BM samples were classified as hyperplastic, 15.1% were
mental Beagles. Use of a 15-gauge needle to obtain a humeral dysplastic, 13.8% were normal, 11.2% were hematopoietic
BM biopsy was significantly easier than obtaining a humeral malignancies, and 9.9% were aplastic/hypoplastic (Turinelli
BM biopsy using a 13-gauge needle or an iliac BM biopsy and Gavazza, 2018).
using a 15-gauge needle. The quality of the biopsies obtained
with a 13-gauge needle was better than for biopsies of BONE MARROW APLASIA-HYPOPLASIA
the humerus or ilium using a 15-gauge needle. Only sites BM aplasia-hypoplasia is a disorder characterized by pe-
sampled with a 13-gauge needle were identifiable grossly ripheral blood cytopenias and a paucity or absence of
after the procedure. In most biopsies, cell density and cel- hematopoietic precursors in the BM. As noted, BM aplasia-
lularity were lower when a 15-gauge needle was used. hypoplasia is commonly associated with the administration
Weiss (2006) reviewed BM aspirates, core biopsies, and of certain drugs, such as griseofulvin or chloramphenicol
medical records of 717 dogs evaluated for presumptive BM in cats and phenylbutazone or estrogen in dogs. It is also
disorders. Approximately 2% of the specimens evaluated commonly associated with infectious diseases, such as ca-
were nondiagnostic, 22% were normal, 26% had changes nine monocytic ehrlichiosis, leishmaniasis, and FeLV infec-
secondary to another primary disease, 24% had nondysplas- tion. A corticosteroid-responsive syndrome of combined
tic and nonneoplastic conditions, 9% had dysplasia, and 18% cytopenias or pancytopenia has been recognized in dogs
had neoplasia. Less than 5% of the specimens evaluated had and cats in our clinic. Some of these patients with pancy-
BM hypoplasia and approximately 20% were hyperplastic; topenia have hypercellular BM (see later), suggesting that
acute leukemias were more common than chronic leukemias. the cells are destroyed peripherally or at the late stages of
Turinelli et al. recently reviewed the cytomorphologic BM production.
findings in BM aspirates in both dogs (Turinelli et al., 2015) BM aspirates from dogs and cats with BM aplasia or
and cats (Turinelli and Gavazza, 2018). Seventy percent of hypoplasia typically show hypocellularity or acellularity, and
295 canine BM samples were diagnostic; 25% were classified a BM biopsy is frequently necessary to obtain specimens for
as BM (myeloid and or erythroid) hyperplasia, 19.3% were histopathologic analysis so that a definitive diagnosis can
normal, 12.9% had hematopoietic malignancy, 7.8% had be made. Once infectious diseases (e.g., Ehrlichia canis titer
aplasia/hypoplasia, and 1.3% had dysplasia. In cats, 46.7% of or rapid assay, FeLV p27 determination) and drug exposure