Page 506 - Anatomy and Physiology of Farm Animals, 8th Edition
P. 506
Pregnancy and Parturition / 491
the period of sexual receptivity (estrus) of Gamete Fusion and Early Embryonic
the female. Motility may last somewhat
VetBooks.ir longer than fertility and the duration of Development
fertile spermatozoa in the female tract is as
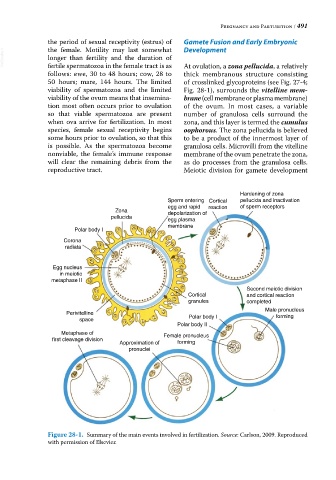
follows: ewe, 30 to 48 hours; cow, 28 to At ovulation, a zona pellucida, a relatively
thick membranous structure consisting
50 hours; mare, 144 hours. The limited of crosslinked glycoproteins (see Fig. 27‐4;
viability of spermatozoa and the limited Fig. 28‐1), surrounds the vitelline mem-
viability of the ovum means that insemina- brane (cell membrane or plasma membrane)
tion most often occurs prior to ovulation of the ovum. In most cases, a variable
so that viable spermatozoa are present number of granulosa cells surround the
when ova arrive for fertilization. In most zona, and this layer is termed the cumulus
species, female sexual receptivity begins oophorous. The zona pellucida is believed
some hours prior to ovulation, so that this to be a product of the innermost layer of
is possible. As the spermatozoa become granulosa cells. Microvilli from the vitelline
nonviable, the female’s immune response membrane of the ovum penetrate the zona,
will clear the remaining debris from the as do processes from the granulosa cells.
reproductive tract. Meiotic division for gamete development
Hardening of zona
Sperm entering Cortical pellucida and inactivation
egg and rapid reaction of sperm receptors
Zona depolarization of
pellucida
egg plasma
membrane
Polar body I
Corona
radiata
Egg nucleus
in meiotic
metaphase II
Second meiotic division
Cortical and cortical reaction
granules completed
Male pronucleus
Perivitelline forming
space Polar body I
Polar body II
Metaphase of Female pronucleus
first cleavage division
Approximation of forming
pronuclei
Figure 28-1. Summary of the main events involved in fertilization. Source: Carlson, 2009. Reproduced
with permission of Elsevier.