Page 1274 - Veterinary Immunology, 10th Edition
P. 1274
VetBooks.ir
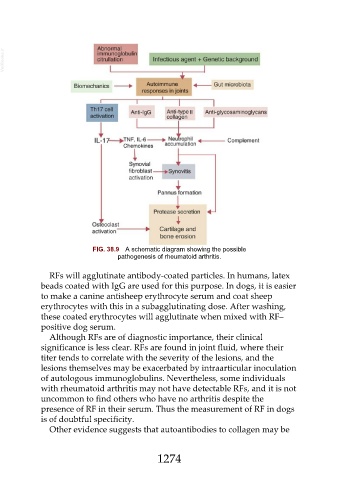
FIG. 38.9 A schematic diagram showing the possible
pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis.
RFs will agglutinate antibody-coated particles. In humans, latex
beads coated with IgG are used for this purpose. In dogs, it is easier
to make a canine antisheep erythrocyte serum and coat sheep
erythrocytes with this in a subagglutinating dose. After washing,
these coated erythrocytes will agglutinate when mixed with RF–
positive dog serum.
Although RFs are of diagnostic importance, their clinical
significance is less clear. RFs are found in joint fluid, where their
titer tends to correlate with the severity of the lesions, and the
lesions themselves may be exacerbated by intraarticular inoculation
of autologous immunoglobulins. Nevertheless, some individuals
with rheumatoid arthritis may not have detectable RFs, and it is not
uncommon to find others who have no arthritis despite the
presence of RF in their serum. Thus the measurement of RF in dogs
is of doubtful specificity.
Other evidence suggests that autoantibodies to collagen may be
1274