Page 1452 - Veterinary Immunology, 10th Edition
P. 1452
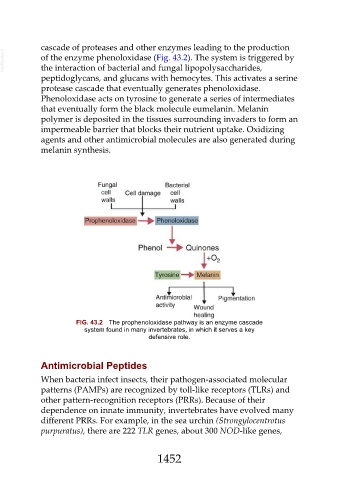
cascade of proteases and other enzymes leading to the production
VetBooks.ir of the enzyme phenoloxidase (Fig. 43.2). The system is triggered by
the interaction of bacterial and fungal lipopolysaccharides,
peptidoglycans, and glucans with hemocytes. This activates a serine
protease cascade that eventually generates phenoloxidase.
Phenoloxidase acts on tyrosine to generate a series of intermediates
that eventually form the black molecule eumelanin. Melanin
polymer is deposited in the tissues surrounding invaders to form an
impermeable barrier that blocks their nutrient uptake. Oxidizing
agents and other antimicrobial molecules are also generated during
melanin synthesis.
FIG. 43.2 The prophenoloxidase pathway is an enzyme cascade
system found in many invertebrates, in which it serves a key
defensive role.
Antimicrobial Peptides
When bacteria infect insects, their pathogen-associated molecular
patterns (PAMPs) are recognized by toll-like receptors (TLRs) and
other pattern-recognition receptors (PRRs). Because of their
dependence on innate immunity, invertebrates have evolved many
different PRRs. For example, in the sea urchin (Strongylocentrotus
purpuratus), there are 222 TLR genes, about 300 NOD-like genes,
1452