Page 360 - The Veterinary Laboratory and Field Manual 3rd Edition
P. 360
Clinical chemistry 329
should be frozen at –20°C. Repeated freezing or is also useful to assess the health of a popula-
thawing may damage stored samples and lead to tion, for example, samples can be collected from
false results in future tests so, since serum banks a representative percentage of animals in an area
are valuable, there should be a reliable alternative to assess the levels of serum trace elements (for
power supply available in case of electricity cuts. example, copper) or mineral levels (for example,
magnesium) especially in areas where nutri-
ent deficiencies have occurred in the past or in
7.3 General health assessment high producing stock that may be susceptible to
metabolic diseases.
Serum biochemistry may be used for routine Advances in technology have resulted in the
assessment of an animal’s health or to assist in development of semi-automated systems (see
the process of confirming a clinical diagnosis. It also Chapter 2) that allow full serum biochemistry
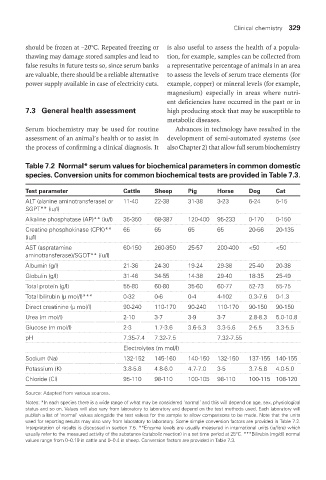
Table 7.2 Normal* serum values for biochemical parameters in common domestic
species. Conversion units for common biochemical tests are provided in Table 7.3.
Test parameter Cattle Sheep Pig Horse dog Cat
ALT (alanine aminotransferase) or 11-40 22-38 31-38 3-23 6-24 5-15
SGPT** (iu/l)
Alkaline phosphatase (AP)** (iu/l) 35-350 68-387 120-400 95-233 0-170 0-150
Creatine phosphokinase (CPK)** 65 65 65 65 20-56 20-135
(iu/l)
AST (aspratamine 60-150 260-350 25-57 200-400 <50 <50
aminotransferase)/SGOT** (iu/l)
Albumin (g/l) 21-36 24-30 19-24 29-38 25-40 20-38
Globulin (g/l) 31-46 34-55 14-38 29-40 18-35 25-49
Total protein (g/l) 55-80 60-80 35-60 60-77 52-73 55-75
Total bilirubin (µ mol/l)*** 0-32 0-6 0-4 4-102 0.3-7.6 0-1.3
Direct creatinine (µ mol/l) 90-240 110-170 90-240 110-170 90-150 90-150
Urea (m mol/l) 2-10 3-7 3-9 3-7 2.8-8.3 5.0-10.8
Glucose (m mol/l) 2-3 1.7-3.6 3.6-5.3 3.3-5.6 2-5.5 3.3-5.5
pH 7.35-7.4 7.32-7.5 7.32-7.55
Electrolytes (m mol/l)
Sodium (Na) 132-152 145-160 140-150 132-150 137-155 140-155
Potassium (K) 3.8-5.8 4.8-6.0 4.7-7.0 3-5 3.7-5.8 4.0-5.0
Chloride (Cl) 95-110 98-110 100-105 98-110 100-115 108-120
Source: Adapted from various sources.
Notes: *In each species there is a wide range of what may be considered ‘normal’ and this will depend on age, sex, physiological
status and so on. Values will also vary from laboratory to laboratory and depend on the test methods used. Each laboratory will
publish a list of ‘normal’ values alongside the test values for the sample to allow comparisons to be made. Note that the units
used for reporting results may also vary from laboratory to laboratory. Some simple conversion factors are provided in Table 7.2.
Interpretation of results is discussed in section 7.5. **Enzyme levels are usually measured in international units (iu/litre) which
usually refer to the measured activity of the substance (catabolic reaction) in a set time period at 25°C. ***Bilirubin (mg/dl) normal
values range from 0–0.19 in cattle and 0–0.4 in sheep. Conversion factors are provided in Table 7.3.
Vet Lab.indb 329 26/03/2019 10:26