Page 1131 - Adams and Stashak's Lameness in Horses, 7th Edition
P. 1131
Foot Care and Farriery 1097
VetBooks.ir
A B
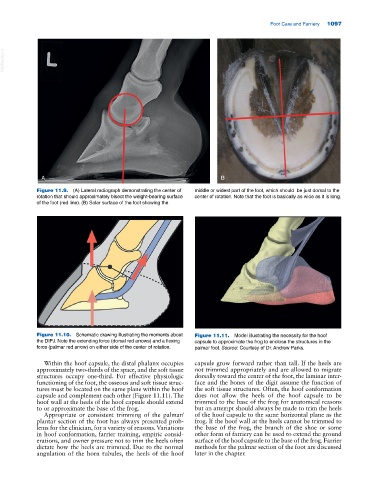
Figure 11.9. (A) Lateral radiograph demonstrating the center of middle or widest part of the foot, which should be just dorsal to the
rotation that should approximately bisect the weight‐bearing surface center of rotation. Note that the foot is basically as wide as it is long.
of the foot (red line). (B) Solar surface of the foot showing the
Figure 11.10. Schematic drawing illustrating the moments about Figure 11.11. Model illustrating the necessity for the hoof
the DIPJ. Note the extending force (dorsal red arrows) and a flexing capsule to approximate the frog to enclose the structures in the
force (palmar red arrow) on either side of the center of rotation. palmar foot. Source: Courtesy of Dr. Andrew Parks.
Within the hoof capsule, the distal phalanx occupies capsule grow forward rather than tall. If the heels are
approximately two‐thirds of the space, and the soft tissue not trimmed appropriately and are allowed to migrate
structures occupy one‐third. For effective physiologic dorsally toward the center of the foot, the laminar inter
functioning of the foot, the osseous and soft tissue struc face and the bones of the digit assume the function of
tures must be located on the same plane within the hoof the soft tissue structures. Often, the hoof conformation
capsule and complement each other (Figure 11.11). The does not allow the heels of the hoof capsule to be
hoof wall at the heels of the hoof capsule should extend trimmed to the base of the frog for anatomical reasons
to or approximate the base of the frog. but an attempt should always be made to trim the heels
Appropriate or consistent trimming of the palmar/ of the hoof capsule to the same horizontal plane as the
plantar section of the foot has always presented prob frog. If the hoof wall at the heels cannot be trimmed to
lems for the clinician, for a variety of reasons. Variations the base of the frog, the branch of the shoe or some
in hoof conformation, farrier training, empiric consid other form of farriery can be used to extend the ground
erations, and owner pressure not to trim the heels often surface of the hoof capsule to the base of the frog. Farrier
dictate how the heels are trimmed. Due to the normal methods for the palmar section of the foot are discussed
angulation of the horn tubules, the heels of the hoof later in the chapter.