Page 304 - Anatomy and Physiology of Farm Animals, 8th Edition
P. 304
Blood and Other Body Fluids / 289
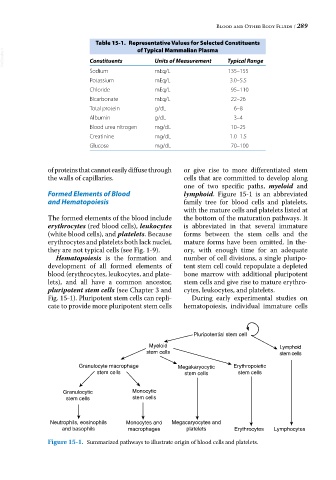
Table 15-1. Representative Values for Selected Constituents
of Typical Mammalian Plasma
VetBooks.ir Constituents Units of Measurement Typical Range
Sodium mEq/L 135–155
Potassium mEq/L 3.0–5.5
Chloride mEq/L 95–110
Bicarbonate mEq/L 22–26
Total protein g/dL 6–8
Albumin g/dL 3–4
Blood urea nitrogen mg/dL 10–25
Creatinine mg/dL 1.0–1.5
Glucose mg/dL 70–100
of proteins that cannot easily diffuse through or give rise to more differentiated stem
the walls of capillaries. cells that are committed to develop along
one of two specific paths, myeloid and
Formed Elements of Blood lymphoid. Figure 15‐1 is an abbreviated
and Hematopoiesis family tree for blood cells and platelets,
with the mature cells and platelets listed at
The formed elements of the blood include the bottom of the maturation pathways. It
erythrocytes (red blood cells), leukocytes is abbreviated in that several immature
(white blood cells), and platelets. Because forms between the stem cells and the
erythrocytes and platelets both lack nuclei, mature forms have been omitted. In the-
they are not typical cells (see Fig. 1‐9). ory, with enough time for an adequate
Hematopoiesis is the formation and number of cell divisions, a single pluripo-
development of all formed elements of tent stem cell could repopulate a depleted
blood (erythrocytes, leukocytes, and plate- bone marrow with additional pluripotent
lets), and all have a common ancestor, stem cells and give rise to mature erythro-
pluripotent stem cells (see Chapter 3 and cytes, leukocytes, and platelets.
Fig. 15‐1). Pluripotent stem cells can repli- During early experimental studies on
cate to provide more pluripotent stem cells hematopoiesis, individual immature cells
Pluripotential stem cell
Myeloid Lymphoid
stem cells stem cells
Granulocyte macrophage Megakaryocytic Erythropoietic
stem cells stem cells stem cells
Granulocytic Monocytic
stem cells stem cells
Neutrophils, eosinophils Monocytes and Megacaryocytes and
and basophils macrophages platelets Erythrocytes Lymphocytes
Figure 15-1. Summarized pathways to illustrate origin of blood cells and platelets.