Page 313 - Anatomy and Physiology of Farm Animals, 8th Edition
P. 313
298 / Anatomy and Physiology of Farm Animals
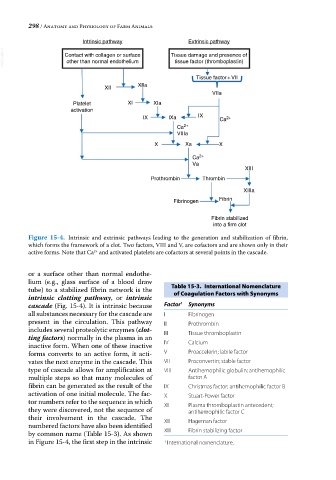
Intrinsic pathway Extrinsic pathway
VetBooks.ir Contact with collagen or surface Tissue damage and presence of
other than normal endothelium
tissue factor (thromboplastin)
Tissue factor +VII
XIIa
XII
VIIa
Platelet XI XIa
activation
IX IXa IX Ca 2+
Ca 2+
VIIIa
X Xa X
Ca 2+
Va
XIII
Prothrombin Thrombin
XIIIa
Fibrinogen Fibrin
Fibrin stabilized
into a firm clot
Figure 15-4. Intrinsic and extrinsic pathways leading to the generation and stabilization of fibrin,
which forms the framework of a clot. Two factors, VIII and V, are cofactors and are shown only in their
active forms. Note that Ca and activated platelets are cofactors at several points in the cascade.
2+
or a surface other than normal endothe-
lium (e.g., glass surface of a blood draw Table 15-3. International Nomenclature
tube) to a stabilized fibrin network is the of Coagulation Factors with Synonyms
intrinsic clotting pathway, or intrinsic
cascade (Fig. 15‐4). It is intrinsic because Factor 1 Synonyms
all substances necessary for the cascade are I Fibrinogen
present in the circulation. This pathway II Prothrombin
includes several proteolytic enzymes (clot III Tissue thromboplastin
ting factors) normally in the plasma in an
inactive form. When one of these inactive IV Calcium
forms converts to an active form, it acti- V Proaccelerin; labile factor
vates the next enzyme in the cascade. This VII Proconvertin; stable factor
type of cascade allows for amplification at VIII Antihemophilic globulin; antihemophilic
multiple steps so that many molecules of factor A
fibrin can be generated as the result of the IX Christmas factor; antihemophilic factor B
activation of one initial molecule. The fac- X Stuart‐Power factor
tor numbers refer to the sequence in which XI Plasma thromboplastin antecedent;
they were discovered, not the sequence of antihemophilic factor C
their involvement in the cascade. The XII Hageman factor
numbered factors have also been identified
by common name (Table 15‐3). As shown XIII Fibrin stabilizing factor
in Figure 15‐4, the first step in the intrinsic 1 International nomenclature.