Page 320 - Anatomy and Physiology of Farm Animals, 8th Edition
P. 320
Body Defenses and the Immune System / 305
APC cell Helper T cell Cell with
MHC I and
with MHC II
VetBooks.ir Antigen B cell Cytotoxic T cell antigen
T H
B T C
B T H T C
Cytokines Cytokines
Proliferation of Proliferation of
B memory Plasma cells helper T cells cytotoxic T cells
cells and production and production
of helper T of cytotoxic T
Antibodies memory cells memory cells
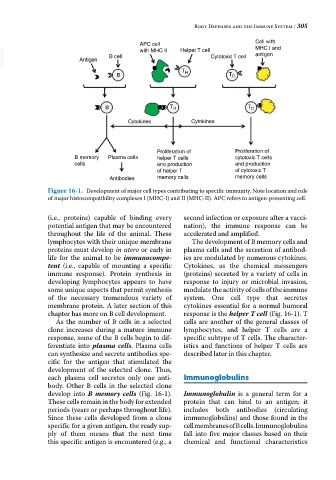
Figure 16-1. Development of major cell types contributing to specific immunity. Note location and role
of major histocompatibility complexes I (MHC‐I) and II (MHC‐II). APC refers to antigen‐presenting cell.
(i.e., proteins) capable of binding every second infection or exposure after a vacci-
potential antigen that may be encountered nation), the immune response can be
throughout the life of the animal. These accelerated and amplified.
lymphocytes with their unique membrane The development of B memory cells and
proteins must develop in utero or early in plasma cells and the secretion of antibod-
life for the animal to be immunocompe- ies are modulated by numerous cytokines.
tent (i.e., capable of mounting a specific Cytokines, as the chemical messengers
immune response). Protein synthesis in (proteins) secreted by a variety of cells in
developing lymphocytes appears to have response to injury or microbial invasion,
some unique aspects that permit synthesis modulate the activity of cells of the immune
of the necessary tremendous variety of system. One cell type that secretes
membrane protein. A later section of this cytokines essential for a normal humoral
chapter has more on B cell development. response is the helper T cell (Fig. 16‐1). T
As the number of B cells in a selected cells are another of the general classes of
clone increases during a mature immune lymphocytes, and helper T cells are a
response, some of the B cells begin to dif- specific subtype of T cells. The character-
ferentiate into plasma cells. Plasma cells istics and functions of helper T cells are
can synthesize and secrete antibodies spe- described later in this chapter.
cific for the antigen that stimulated the
development of the selected clone. Thus,
each plasma cell secretes only one anti- Immunoglobulins
body. Other B cells in the selected clone
develop into B memory cells (Fig. 16‐1). Immunoglobulin is a general term for a
These cells remain in the body for extended protein that can bind to an antigen; it
periods (years or perhaps throughout life). includes both antibodies (circulating
Since these cells developed from a clone immunoglobulins) and those found in the
specific for a given antigen, the ready sup- cell membranes of B cells. Immunoglobulins
ply of them means that the next time fall into five major classes based on their
this specific antigen is encountered (e.g., a chemical and functional characteristics