Page 100 - Clinical Small Animal Internal Medicine
P. 100
68 Section 2 Endocrine Disease
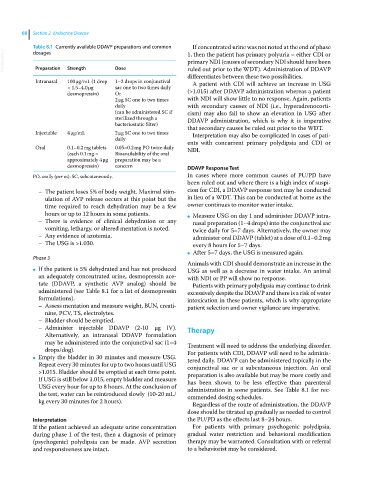
Table 8.1 Currently available DDAVP preparations and common If concentrated urine was not noted at the end of phase
VetBooks.ir Preparation Strength Dose 1, then the patient has primary polyuria – either CDI or
dosages
primary NDI (causes of secondary NDI should have been
ruled out prior to the WDT). Administration of DDAVP
differentiates between these two possibilities.
Intranasal 100 μg/mL (1 drop 1–2 drops in conjunctival A patient with CDI will achieve an increase in USG
= 1.5–4.0 μg sac one to two times daily
desmopressin) Or (>1.015) after DDAVP administration whereas a patient
2 μg SC one to two times with NDI will show little to no response. Again, patients
daily with secondary causes of NDI (i.e., hyperadrenocorti-
(can be administered SC if cism) may also fail to show an elevation in USG after
sterilized through a DDAVP administration, which is why it is imperative
bacteriostatic filter) that secondary causes be ruled out prior to the WDT.
Injectable 4 μg/mL 2 μg SC one to two times Interpretation may also be complicated in cases of pati-
daily ents with concurrent primary polydipsia and CDI or
Oral 0.1–0.2 mg tablets 0.05–0.2 mg PO twice daily NDI.
(each 0.1 mg = Bioavailability of the oral
approximately 4 μg preparation may be a
desmopressin) concern DDAVP Response Test
PO, orally (per os); SC, subcutaneously. In cases where more common causes of PU/PD have
been ruled out and where there is a high index of suspi-
– The patient loses 5% of body weight. Maximal stim- cion for CDI, a DDAVP response test may be conducted
ulation of AVP release occurs at this point but the in lieu of a WDT. This can be conducted at home as the
time required to reach dehydration may be a few owner continues to monitor water intake.
hours or up to 12 hours in some patients. Measure USG on day 1 and administer DDAVP intra-
– There is evidence of clinical dehydration or any ● nasal preparation (1–4 drops) into the conjunctival sac
vomiting, lethargy, or altered mentation is noted. twice daily for 5–7 days. Alternatively, the owner may
– Any evidence of azotemia. administer oral DDAVP (tablet) at a dose of 0.1–0.2 mg
– The USG is >1.030. every 8 hours for 5–7 days.
After 5–7 days, the USG is measured again.
●
Phase 3
Animals with CDI should demonstrate an increase in the
If the patient is 5% dehydrated and has not produced
● USG as well as a decrease in water intake. An animal
an adequately concentrated urine, desmopressin ace- with NDI or PP will show no response.
tate (DDAVP, a synthetic AVP analog) should be Patients with primary polydipsia may continue to drink
administered (see Table 8.1 for a list of desmopressin excessively despite the DDAVP and there is a risk of water
formulations). intoxication in these patients, which is why appropriate
– Assess mentation and measure weight, BUN, creati- patient selection and owner vigilance are imperative.
nine, PCV, TS, electrolytes.
– Bladder should be emptied.
– Administer injectable DDAVP (2-10 μg IV). Therapy
Alternatively, an intranasal DDAVP formulation
may be administered into the conjunctival sac (1–4 Treatment will need to address the underlying disorder.
drops/dog). For patients with CDI, DDAVP will need to be adminis-
Empty the bladder in 30 minutes and measure USG.
● tered daily. DDAVP can be administered topically in the
Repeat every 30 minutes for up to two hours until USG conjunctival sac or a subcutaneous injection. An oral
>1.015. Bladder should be emptied at each time point. preparation is also available but may be more costly and
If USG is still below 1.015, empty bladder and measure has been shown to be less effective than parenteral
USG every hour for up to 8 hours. At the conclusion of administration in some patients. See Table 8.1 for rec-
the test, water can be reintroduced slowly (10-20 mL/ ommended dosing schedules.
kg every 30 minutes for 2 hours). Regardless of the route of administration, the DDAVP
dose should be titrated up gradually as needed to control
Interpretation the PU/PD as the effects last 8–24 hours.
If the patient achieved an adequate urine concentration For patients with primary psychogenic polydipsia,
during phase 1 of the test, then a diagnosis of primary gradual water restriction and behavioral modification
(psychogenic) polydipsia can be made. AVP secretion therapy may be warranted. Consultation with or referral
and responsiveness are intact. to a behaviorist may be considered.