Page 130 - Clinical Small Animal Internal Medicine
P. 130
98 Section 2 Endocrine Disease
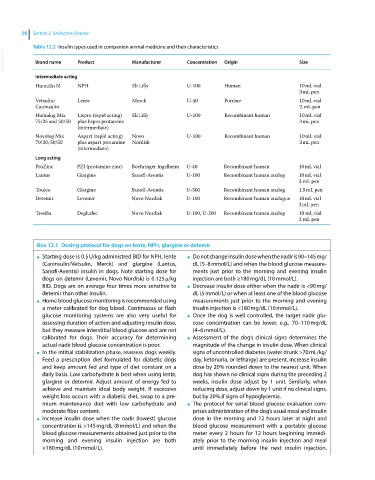
Table 12.2 Insulin types used in companion animal medicine and their characteristics
VetBooks.ir Brand name Product Manufacturer Concentration Origin Size
Intermediate acting
Humulin N NPH Eli Lilly U‐100 Human 10 mL vial
3 mL pen
Vetsulin/ Lente Merck U‐40 Porcine 10 mL vial
Caninsulin 2. mL pen
Humalog Mix Lispro (rapid acting) Eli Lilly U‐100 Recombinant human 10 mL vial
75/25 and 50/50 plus lispro protamine 3 mL pen
(intermediate)
Novolog Mix Aspart (rapid acting) Novo U‐100 Recombinant human 10 mL vial
70/30; 50/50 plus aspart protamine Nordisk 3 mL pen
(intermediate)
Long acting
ProZinc PZI (protamine zinc) Boehringer Ingelheim U‐40 Recombinant human 10 mL vial
Lantus Glargine Sanofi‐Aventis U‐100 Recombinant human analog 10 mL vial
3 mL pen
Toujeo Glargine Sanofi‐Aventis U‐300 Recombinant human analog 1.5 mL pen
Detemir Levemir Novo Nordisk U‐100 Recombinant human analogue 10 mL vial
3 mL pen
Tresiba Degludec Novo Nordisk U‐100, U‐200 Recombinant human analog 10 mL vial
3 mL pen
Box 12.1 Dosing protocol for dogs on lente, NPH, glargine or detemir
● Starting dose is 0.5 U/kg administred BID for NPH, lente ● Do not change insulin dose when the nadir is 90–145 mg/
(Caninsulin/Vetsulin, Merck) and glargine (Lantus, dL (5–8 mmol/L) and when the blood glucose measure-
Sanofi‐Aventis) insulin in dogs. Note starting dose for ments just prior to the morning and evening insulin
dogs on detemir (Levemir, Novo Nordisk) is 0.125 μ/kg injection are both ≥180 mg/dL (10 mmol/L).
BID. Dogs are on average four times more sensitive to ● Decrease insulin dose either when the nadir is <90 mg/
detemir than other insulin. dL (5 mmol/L) or when at least one of the blood glucose
● Home blood glucose monitoring is recommended using measurements just prior to the morning and evening
a meter calibrated for dog blood. Continuous or flash insulin injection is <180 mg/dL (10 mmol/L).
glucose monitoring systems are also very useful for ● Once the dog is well controlled, the target nadir glu-
assessing duration of action and adjusting insulin dose, cose concentration can be lower, e.g., 70–110 mg/dL
but they measure interstitial blood glucose and are not (4–6 mmol/L).
calibrated for dogs. Their accuracy for determining ● Assessment of the dog’s clinical signs determines the
actual nadir blood glucose concentration is poor. magnitude of the change in insulin dose. When clinical
● In the intitial stabilization phase, reassess dogs weekly. signs of uncontrolled diabetes (water drunk >70 mL/kg/
Feed a prescription diet formulated for diabetic dogs day, ketonuria, or lethargy) are present, increase insulin
and keep amount fed and type of diet constant on a dose by 20% rounded down to the nearest unit. When
daily basis. Low carbohydrate is best when using lente, dog has shown no clinical signs during the preceding 2
glargine or determir. Adjust amount of energy fed to weeks, insulin dose adjust by 1 unit. Similarly, when
achieve and maintain ideal body weight. If excessive reducing dose, adjust down by 1 unit if no clinical signs,
weight loss occurs with a diabetic diet, swap to a pre- but by 20% if signs of hypoglycemia.
mium maintenance diet with low carbohydrate and ● The protocol for serial blood glucose evaluation com-
moderate fiber content. prises administration of the dog’s usual meal and insulin
● Increase insulin dose when the nadir (lowest) glucose dose in the morning and 12 hours later at night and
concentration is >145 mg/dL (8 mmol/L) and when the blood glucose measurement with a portable glucose
blood glucose measurements obtained just prior to the meter every 2 hours for 12 hours beginning immedi-
morning and evening insulin injection are both ately prior to the morning insulin injection and meal
≥180 mg/dL (10 mmol/L). until immediately before the next insulin injection.