Page 259 - Clinical Small Animal Internal Medicine
P. 259
23 Pulmonary Hypertension 227
Right Heart Catheterization On the other hand, thoracic radiographs may only show
VetBooks.ir Right heart catheterization is the gold standard in diag- changes that represent the underlying disease process
that results in PH development (i.e., left‐sided heart dis-
nosing PH. Unfortunately, in veterinary medicine right
heart catheterization is usually prohibitive due to the ease, left‐sided congestive heart failure, primary pulmo-
nary disease, patent ductus arteriosus). Noncardiogenic
need for sedation and the unacceptable level of invasive- pulmonary edema can form as a direct result of PH and is
ness required. Right heart catheterization provides true typically in a patchy, diffuse alveolar lung pattern.
measurements of pulmonary artery pressure, right ven-
tricular pressure, right atrial pressure, and pulmonary
capillary wedge pressure. In addition, cardiac output Electrocardiogram
measurements can be obtained to calculate pulmonary
vascular resistance. Pulmonary vascular resistance The electrocardiogram is of limited use in contributing
(PVR) can be calculated by the following equation and to PH diagnosis. If there are findings of a right axis devia-
−5
expressed as dynes*sec*cm . tion or evidence of right heart enlargement, this would
help support the diagnosis of PH (Figure 23.3).
PVR mPAP PCWP 80 /CO
Echocardiogram
where mPAP indicates mean pulmonary artery pressure,
PCWP is pulmonary capillary wedge pressure, and CO is Echocardiography is the standard, noninvasive method
cardiac output. Measuring and calculating mPAP, PCWP, for quantifying and diagnosing PH in veterinary medi-
and PVR help to determine the etiology of the PH. Based cine. Tricuspid regurgitation enables the clinician to
on these measurements, PH can be further classified as estimate the systolic pulmonary artery pressure
pulmonary arterial or venous hypertension. Pulmonary (Figure 23.4) and pulmonic insufficiency provides esti-
arterial hypertension can be diagnosed if the mPAP is mation of the mean and diastolic pulmonary artery
increased, the PVR is elevated, and the PCWP is normal. pressures (Figure 23.5).
Pulmonary venous hypertension can be diagnosed if the Based on tricuspid regurgitation, PH can be classified as
mPAP is increased, the PVR is normal, and the PCWP is mild (≥2.8 to <3.5 m/s, ≥31 to <50 mmHg), moderate (3.5–
elevated. 4.3 m/s, 50–75 mmHg) or severe (>4.3 m/s, >75 mmHg).
Multiple two‐dimensional, M‐mode, and Doppler echo-
Thoracic Radiography cardiographic findings support the diagnosis of PH when
tricuspid regurgitation is or is not present, and they
Pulmonary hypertension cannot be diagnosed by thoracic include interventricular septal flattening (Figure 23.6),
radiographs but there are specific changes associated with right ventricular hypertrophy, right ventricular dilation,
PH that, when present, would support the diagnosis of decreased tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion, main
PH. Right heart enlargement, pulmonary artery enlarge- pulmonary artery enlargement, abnormal pulmonary
ment, and pulmonary artery tortuosity are abnormalities artery flow profiles, and decreased relative area change
that may suggest the presence of PH (Figure 23.2). (a.k.a. distensibility index) of the right pulmonary artery.
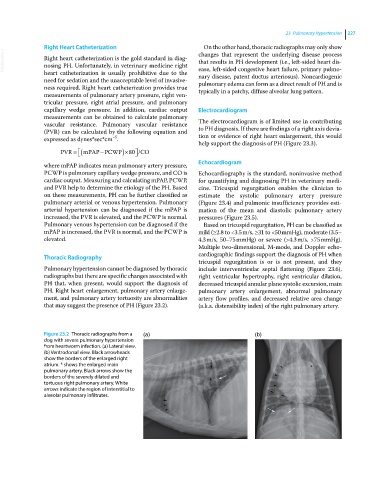
Figure 23.2 Thoracic radiographs from a (a) (b)
dog with severe pulmonary hypertension
from heartworm infection. (a) Lateral view.
(b) Ventrodorsal view. Black arrowheads
show the borders of the enlarged right
atrium. * shows the enlarged main
pulmonary artery. Black arrows show the
borders of the severely dilated and
tortuous right pulmonary artery. White
arrows indicate the region of interstitial to
alveolar pulmonary infiltrates.