Page 275 - Clinical Small Animal Internal Medicine
P. 275
24 Congenital Heart Disease 243
In the author’s experience, right‐sided CHF will com- The decision to operate or pursue transcatheter therapy
VetBooks.ir monly need higher doses of oral furosemide or an alter- relates to the expertise of the veterinarian performing
the procedure, anatomy of the defect, and client prefer-
native diuretic such as torsemide due to the potential for
intestinal edema causing decreased gastrointestinal
erinary medicine, though retrospective data on PDA
absorption. ACE inhibitors should always be used in the ence. Prospective comparison studies are lacking in vet-
treatment of chronic CHF to decrease RAAS activation closure suggest comparable to improved outcomes from
associated with advanced heart failure and diuretic a transcatheter approach compared to surgery. Novel
administration. devices, such as the Amplatz™ canine ductal occluder,
Pimobendan has become standard of care in the treat- have greatly improved the ease with which PDA occlu-
ment of CHF secondary to acquired cardiac diseases, sion can be performed from a transarterial approach
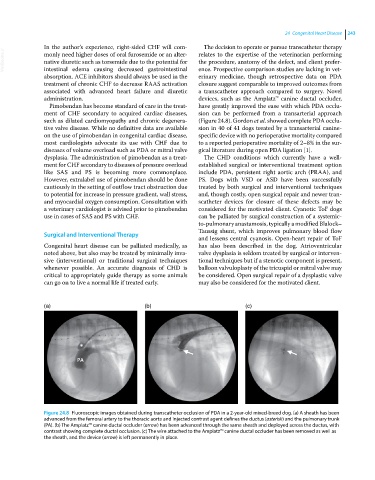
such as dilated cardiomyopathy and chronic degenera- (Figure 24.8). Gordon et al. showed complete PDA occlu-
tive valve disease. While no definitive data are available sion in 40 of 41 dogs treated by a transarterial canine‐
on the use of pimobendan in congenital cardiac disease, specific device with no perioperative mortality compared
most cardiologists advocate its use with CHF due to to a reported perioperative mortality of 2–8% in the sur-
diseases of volume overload such as PDA or mitral valve gical literature during open PDA ligation [1].
dysplasia. The administration of pimobendan as a treat- The CHD conditions which currently have a well‐
ment for CHF secondary to diseases of pressure overload established surgical or interventional treatment option
like SAS and PS is becoming more commonplace. include PDA, persistent right aortic arch (PRAA), and
However, extralabel use of pimobendan should be done PS. Dogs with VSD or ASD have been successfully
cautiously in the setting of outflow tract obstruction due treated by both surgical and interventional techniques
to potential for increase in pressure gradient, wall stress, and, though costly, open surgical repair and newer tran-
and myocardial oxygen consumption. Consultation with scatheter devices for closure of these defects may be
a veterinary cardiologist is advised prior to pimobendan considered for the motivated client. Cyanotic ToF dogs
use in cases of SAS and PS with CHF. can be palliated by surgical construction of a systemic‐
to‐pulmonary anastamosis, typically a modified Blalock–
Taussig shunt, which improves pulmonary blood flow
Surgical and Interventional Therapy
and lessens central cyanosis. Open‐heart repair of ToF
Congenital heart disease can be palliated medically, as has also been described in the dog. Atrioventricular
noted above, but also may be treated by minimally inva- valve dysplasia is seldom treated by surgical or interven-
sive (interventional) or traditional surgical techniques tional techniques but if a stenotic component is present,
whenever possible. An accurate diagnosis of CHD is balloon valvuloplasty of the tricuspid or mitral valve may
critical to appropriately guide therapy as some animals be considered. Open surgical repair of a dysplastic valve
can go on to live a normal life if treated early. may also be considered for the motivated client.
(a) (b) (c)
Figure 24.8 Fluoroscopic images obtained during transcatheter occlusion of PDA in a 2‐year‐old mixed‐breed dog. (a) A sheath has been
advanced from the femoral artery to the thoracic aorta and injected contrast agent defines the ductus (asterisk) and the pulmonary trunk
(PA). (b) The Amplatz™ canine ductal occluder (arrow) has been advanced through the same sheath and deployed across the ductus, with
contrast showing complete ductal occlusion. (c) The wire attached to the Amplatz™ canine ductal occluder has been removed as well as
the sheath, and the device (arrow) is left permanently in place.