Page 58 - BSAVA Manual of Canine and Feline Head, Neck and Thoracic Surgery, 2nd Edition
P. 58
Chapter 4 · Surgery of the nose and nasopharynx
WARNING
VetBooks.ir Neoplastic, fungal and inflammatory nasal diseases all
share similar radiographic features
The radiographic appearance of nasal tumours will
change with the duration of the lesion and the histological
type of the tumour. Plain radiography is not a highly
sensitive diagnostic method for identification of the cause
of nasal diseases, especially in cases of early or less
aggressive neoplasia (Saunders et al., 2004; Pownder et
al., 2006; Johnson and Wisner, 2007). Conchal deviation
or destruction, and destruction of the nasal septum, (a)
vomer bone, palatine bone, frontal bone or maxillary
bone are suggestive of neoplasia. The presence of bony
lysis often indicates a poor prognosis. In cats, a unilateral
aggressive lesion that results in lysis of lateral nasal
bones, turbinate destruction or loss of teeth is more likely
to be a neoplasm, whereas a bilaterally symmetrical
lesion is suggestive of chronic rhinitis (Mukaratirwa et al.,
2001; Johnson and Wisner, 2007). Neoplasia may also
cause increased soft tissue opacity both within and out-
side the confines of the nasal cavity, indicating tumour
extension beyond the limits of the nasal cavity. Increased
opacity of the frontal sinus may result from primary
disease or may be secondary to an obstructive rhinitis
and subsequent accumulation of mucus.
In general, fungal disease causes destruction of the
turbinates, decreasing radiographic density or creating (b)
increased lucency within the nasal cavity or nasal bones,
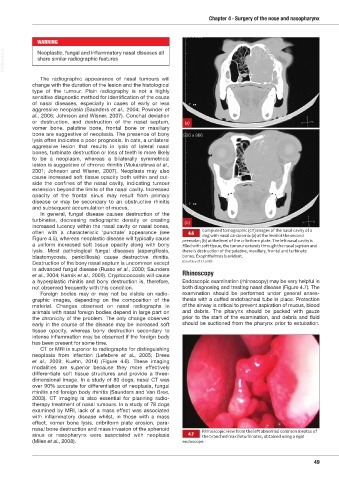
often with a characteristic ‘punctate’ appearance (see 4.6 Computed tomographic (CT) images of the nasal cavity of a
dog with nasal carcinoma: (a) at the level of the second
Figure 4.5), whereas neoplastic disease will typically cause premolar; (b) at the level of the cribriform plate. The left nasal cavity is
a uniform increased soft tissue opacity along with bony filled ith soft tissue the tumour e tends through the nasal septum and
lysis. Most pathological fungal diseases (aspergillosis, there is destruction of the palatine, maxillary, frontal and turbinate
blastomycosis, penicilliosis) cause destructive rhinitis. bones. Exophthalmos is evident.
(Courtesy of C Lamb)
Destruction of the bony nasal septum is uncommon except
in advanced fungal disease (Russo et al., 2000; Saunders Rhinoscopy
et al., 2004; Karnik et al., 2009). Cryptococcosis will cause
a hyperplastic rhinitis and bony destruction is, therefore, Endoscopic examination (rhinoscopy) may be very helpful in
not observed frequently with this condition. both diagnosing and treating nasal disease (Figure 4.7). The
Foreign bodies may or may not be visible on radio- examination should be performed under general anaes-
graphic images, depending on the composition of the thesia with a cuffed endotracheal tube in place. Protection
material. Changes observed on nasal radiographs in of the airway is critical to prevent aspiration of mucus, blood
animals with nasal foreign bodies depend in large part on and debris. The pharynx should be packed with gauze
the chronicity of the problem. The only change observed prior to the start of the examination, and debris and fluid
early in the course of the disease may be increased soft should be suctioned from the pharynx prior to extubation.
tissue opacity, whereas bony destruction secondary to
intense inflammation may be observed if the foreign body
has been present for some time.
CT or MRI is superior to radiographs for distinguishing
neoplasia from infection (Lefebvre et al., 2005; Drees
et al., 2009; Kuehn, 2014) (Figure 4.6). These imaging
modalities are superior because they more effectively
differentiate soft tissue structures and provide a three-
dimensional image. In a study of 80 dogs, nasal CT was
over 90% accurate for differentiation of neoplasia, fungal
rhinitis and foreign body rhinitis (Saunders and Van Bree,
2003). CT imaging is also essential for planning radio-
therapy treatment of nasal tumours. In a study of 78 dogs
examined by MRI, lack of a mass effect was associated
with inflammatory disease whilst, in those with a mass
effect, vomer bone lysis, cribriform plate erosion, para-
nasal bone destruction and mass invasion of the sphenoid Rhinoscopic view from the left abnormal common meatus of
sinus or nasopharynx were associated with neoplasia 4.7 the branched maxilloturbinates, obtained using a rigid
(Miles et al., 2008). endoscope.
49
Ch04 HNT.indd 49 31/08/2018 10:49