Page 444 - Small Animal Clinical Nutrition 5th Edition
P. 444
458 Small Animal Clinical Nutrition
VetBooks.ir
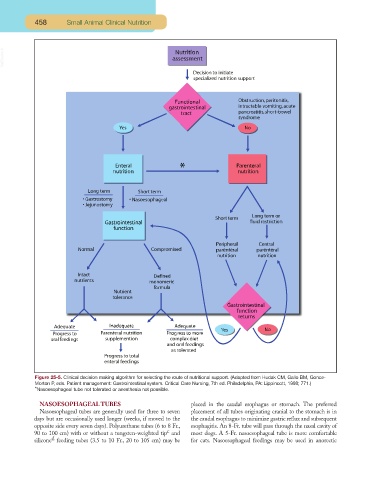
Figure 25-5. Clinical decision making algorithm for selecting the route of nutritional support. (Adapted from Hudak CM, Gallo BM, Gonce-
Morton P, eds. Patient management: Gastrointestinal system. Critical Care Nursing, 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott, 1998; 771.)
*Nasoesophageal tube not tolerated or anesthesia not possible.
NASOESOPHAGEAL TUBES placed in the caudal esophagus or stomach. The preferred
Nasoesophageal tubes are generally used for three to seven placement of all tubes originating cranial to the stomach is in
days but are occasionally used longer (weeks, if moved to the the caudal esophagus to minimize gastric reflux and subsequent
opposite side every seven days). Polyurethane tubes (6 to 8 Fr., esophagitis. An 8-Fr. tube will pass through the nasal cavity of
c
90 to 100 cm) with or without a tungsten-weighted tip and most dogs. A 5-Fr. nasoesophageal tube is more comfortable
d
silicone feeding tubes (3.5 to 10 Fr., 20 to 105 cm) may be for cats. Nasoesophageal feedings may be used in anorectic