Page 386 - Small Animal Clinical Nutrition 5th Edition
P. 386
396 Small Animal Clinical Nutrition
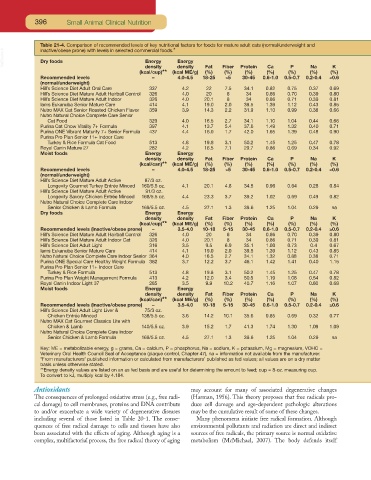
Table 21-4. Comparison of recommended levels of key nutritional factors for foods for mature adult cats (normal/underweight and
inactive/obese prone) with levels in selected commercial foods.*
VetBooks.ir Dry foods Energy Energy
density
density
Na
K
Ca
P
(kcal/cup)** (kcal ME/g) Fat Fiber Protein (%) (%) (%) (%)
(%)
(%)
(%)
Recommended levels – 4.0-4.5 18-25 ≤5 30-45 0.6-1.0 0.5-0.7 0.2-0.4 ≥0.6
(normal/underweight)
Hill’s Science Diet Adult Oral Care 337 4.2 22 7.5 34.1 0.82 0.75 0.37 0.69
Hill’s Science Diet Mature Adult Hairball Control 326 4.0 20 8 34 0.86 0.70 0.39 0.80
Hill’s Science Diet Mature Adult Indoor 326 4.0 20.1 8 34 0.86 0.71 0.39 0.81
Iams Eukanuba Senior Mature Care 414 4.1 19.0 2.0 39.5 1.39 1.12 0.43 0.85
Nutro MAX Cat Senior Roasted Chicken Flavor 359 3.9 14.3 2.2 31.9 1.10 0.99 0.38 0.66
Nutro Natural Choice Complete Care Senior
Cat Food 329 4.0 16.5 2.7 34.1 1.10 1.04 0.44 0.66
Purina Cat Chow Vitality 7+ Formula 397 4.1 13.7 5.4 37.6 1.49 1.32 0.40 0.71
Purina ONE Vibrant Maturity 7+ Senior Formula 437 4.4 16.0 1.7 42.0 1.65 1.39 0.48 0.90
Purina Pro Plan Senior 11+ Indoor Care
Turkey & Rice Formula Cat Food 513 4.8 19.8 3.1 50.2 1.45 1.25 0.47 0.78
Royal Canin Mature 27 282 4.2 16.5 7.1 29.7 0.86 0.69 0.34 0.92
Moist foods Energy Energy
density density Fat Fiber Protein Ca P Na K
(kcal/can)** (kcal ME/g) (%) (%) (%) (%) (%) (%) (%)
Recommended levels – 4.0-4.5 18-25 ≤5 30-45 0.6-1.0 0.5-0.7 0.2-0.4 ≥0.6
(normal/underweight)
Hill’s Science Diet Mature Adult Active 87/3 oz.
Longevity Gourmet Turkey Entrée Minced 160/5.5 oz. 4.1 20.1 4.8 34.5 0.96 0.64 0.28 0.84
Hill’s Science Diet Mature Adult Active 91/3 oz.
Longevity Savory Chicken Entrée Minced 168/5.5 oz. 4.4 23.3 3.7 39.2 1.02 0.69 0.49 0.82
Nutro Natural Choice Complete Care Indoor
Senior Chicken & Lamb Formula 169/5.5 oz. 4.5 27.1 1.3 39.6 1.25 1.04 0.29 na
Dry foods Energy Energy
density density Fat Fiber Protein Ca P Na K
(kcal/cup)** (kcal ME/g) (%) (%) (%) (%) (%) (%) (%)
Recommended levels (inactive/obese prone) – 3.5-4.0 10-18 5-15 30-45 0.6-1.0 0.5-0.7 0.2-0.4 ≥0.6
Hill’s Science Diet Mature Adult Hairball Control 326 4.0 20 8 34 0.86 0.70 0.39 0.80
Hill’s Science Diet Mature Adult Indoor Cat 326 4.0 20.1 8 34 0.86 0.71 0.39 0.81
Hill’s Science Diet Adult Light 316 3.5 9.5 6.9 35.1 1.00 0.73 0.4 0.67
Iams Eukanuba Senior Mature Care 414 4.1 19.0 2.0 39.5 1.39 1.12 0.43 0.85
Nutro Natural Choice Complete Care Indoor Senior 364 4.0 16.5 2.7 34.1 1.32 0.88 0.38 0.71
Purina ONE Special Care Healthy Weight Formula 362 3.7 12.2 3.7 46.1 1.42 1.41 0.40 1.15
Purina Pro Plan Senior 11+ Indoor Care
Turkey & Rice Formula 513 4.8 19.8 3.1 50.2 1.45 1.25 0.47 0.78
Purina Pro Plan Weight Management Formula 413 4.2 12.0 3.4 50.5 1.19 1.08 0.54 0.82
Royal Canin Indoor Light 37 285 3.5 9.9 10.2 40.7 1.16 1.07 0.80 0.68
Moist foods Energy Energy
density density Fat Fiber Protein Ca P Na K
(kcal/can)** (kcal ME/g) (%) (%) (%) (%) (%) (%) (%)
Recommended levels (inactive/obese prone) – 3.5-4.0 10-18 5-15 30-45 0.6-1.0 0.5-0.7 0.2-0.4 ≥0.6
Hill’s Science Diet Adult Light Liver & 75/3 oz.
Chicken Entrée Minced 138/5.5 oz. 3.6 14.2 10.1 35.6 0.85 0.69 0.32 0.77
Nutro MAX Cat Gourmet Classics Lite with
Chicken & Lamb 140/5.5 oz. 3.9 15.2 1.7 41.3 1.74 1.30 1.09 1.09
Nutro Natural Choice Complete Care Indoor
Senior Chicken & Lamb Formula 169/5.5 oz. 4.5 27.1 1.3 39.6 1.25 1.04 0.29 na
Key: ME = metabolizable energy, g = grams, Ca = calcium, P = phosphorus, Na = sodium, K = potassium, Mg = magnesium, VOHC =
Veterinary Oral Health Council Seal of Acceptance (plaque control, Chapter 47), na = information not available from the manufacturer.
*From manufacturers’ published information or calculated from manufacturers’ published as fed values; all values are on a dry matter
basis unless otherwise stated.
**Energy density values are listed on an as fed basis and are useful for determining the amount to feed; cup = 8-oz. measuring cup.
To convert to kJ, multiply kcal by 4.184.
Antioxidants may account for many of associated degenerative changes
The consequences of prolonged oxidative stress (e.g., free radi- (Harman, 1956). This theory proposes that free radicals pro-
cal damage) to cell membranes, proteins and DNA contribute duce cell damage and age-dependent pathologic alterations
to and/or exacerbate a wide variety of degenerative diseases may be the cumulative result of some of these changes.
including several of those listed in Table 20-1. The conse- Many phenomena initiate free radical formation. Although
quences of free radical damage to cells and tissues have also environmental pollutants and radiation are direct and indirect
been associated with the effects of aging. Although aging is a sources of free radicals, the primary source is normal oxidative
complex, multifactorial process, the free radical theory of aging metabolism (McMichael, 2007). The body defends itself