Page 581 - Small Animal Clinical Nutrition 5th Edition
P. 581
602 Small Animal Clinical Nutrition
Box 30-5. Novel Foods, Ingredients and Cancer.
VetBooks.ir PROTEASE INHIBITORS positive mesenteric lymph node and hepatic bacterial cultures (50
Much information suggests that soybean-derived Bowman-Birk and 33%, respectively). Cats fed the soybean protein-based puri-
inhibitor can inhibit or suppress carcinogenesis in vivo and in vitro. fied food had the least villous atrophy (Figure 2) and a significant-
Extracts of the Bowman-Birk inhibitor suppress carcinogenesis in ly smaller magnitude of reduction in WBC counts compared with
several animal model systems, including colon- and liver-induced cats receiving the crystalline amino acid (Figure 3) and casein-
carcinogenesis in mice, anthracene-induced cheek pouch car- based purified foods. Feeding complex (Figure 4) and soybean
cinogenesis in hamsters, lung tumorigenesis in mice and protein-based foods was also associated with the greatest secre-
esophageal carcinogenesis in rats. Bowman-Birk inhibitor concen- tagogue activity on plasma cholecystokinin (CCK) concentrations
tration inhibits metastases and weight loss associated with radia- after ingestion of the respective meals, compared with concentra-
tion-induced thymic lymphoma in mice. Irradiated rodents treated tions in cats receiving the amino acid and casein-based purified
with dietary Bowman-Birk inhibitor have fewer deaths, lower aver- foods. This study showed an association between feeding a soy-
age grade of lymphoma and larger fat stores than controls. bean protein-based purified food and improved intestinal integrity.
Various soy products produce dramatic protection against These findings might be associated with a greater secretogogue
methotrexate (MTX)-induced enterotoxicity in rodent models. effect in stimulating trophic gut hormones such as CCK. In con-
One study was performed using a feline model of MTX-induced trast, the casein-based purified food was associated with
enteritis to determine the impact of purified foods containing increased morbidity, villous atrophy, increased bacterial transloca-
intact protein sources (soybean protein or casein) or crystalline tion and decreased secretogogue activity on CCK. Additional stud-
amino acids on intestinal structure and function. Cats receiving a ies may determine the underlying mechanism of protection and
commercially available (complex) food served as the control the exact compound(s) responsible for soybean protein’s protec-
group. MTX administration was associated with severe enterotox- tive effects.
icity manifested by vomiting and diarrhea, especially in cats
receiving crystalline amino acid and casein-based purified foods. POLYPHENOLIC COMPOUNDS AND FLAVONOIDS
Cats receiving the casein-based purified food had the largest Numerous health benefits result from consumption of diets rich in
decrease in total white blood cell (WBC) and platelet counts, the phytochemicals such as polyphenolic compounds. Polyphenolic
greatest villous atrophy (Figure 1) and the highest incidence of compounds are potent dietary antioxidants and it is thought that
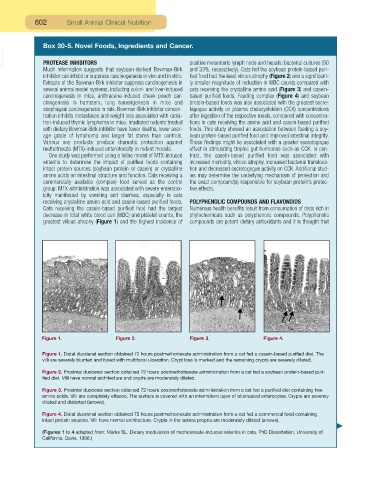
Figure 1. Figure 2. Figure 3. Figure 4.
Figure 1. Distal duodenal section obtained 72 hours postmethotrexate administration from a cat fed a casein-based purified diet. The
villi are severely blunted and fused with multifocal ulceration. Crypt loss is marked and the remaining crypts are severely dilated.
Figure 2. Proximal duodenal section obtained 72 hours postmethotrexate administration from a cat fed a soybean protein-based puri-
fied diet. Villi have normal architecture and crypts are moderately dilated.
Figure 3. Proximal duodenal section obtained 72 hours postmethotrexate administration from a cat fed a purified diet containing free
amino acids. Villi are completely effaced. The surface is covered with an intermittent layer of attenuated enterocytes. Crypts are severely
dilated and distorted (arrows).
Figure 4. Distal duodenal section obtained 72 hours postmethotrexate administration from a cat fed a commercial food containing
intact protein sources. Villi have normal architecture. Crypts in the lamina propria are moderately dilated (arrows).
(Figures 1 to 4 adapted from: Marks SL. Dietary modulation of methotrexate-induced enteritis in cats. PhD Dissertation, University of
California, Davis, 1996.)