Page 81 - Small Animal Clinical Nutrition 5th Edition
P. 81
Macronutrients 81
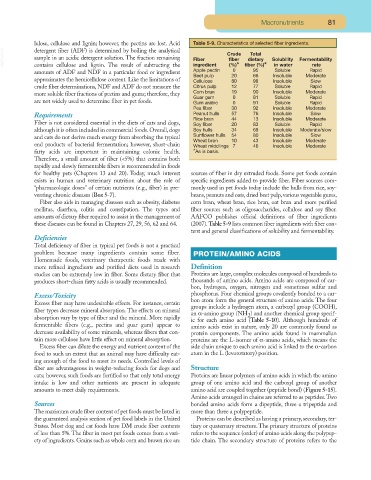
lulose, cellulose and lignin; however, the pectins are lost. Acid Table 5-9. Characteristics of selected fiber ingredients.
VetBooks.ir detergent fiber (ADF) is determined by boiling the analytical Fiber Crude fiber (%)* Solubility Fermentability
Total
sample in an acidic detergent solution. The fraction remaining
dietary
fiber
(%)*
contains cellulose and lignin. The result of subtracting the
in water
ingredient
rate
amounts of ADF and NDF in a particular food or ingredient Apple pectin 0 95 Soluble Rapid
Beet pulp 20 66 Insoluble Moderate
approximates the hemicellulose content. Like the limitations of Cellulose 80 98 Insoluble Slow
crude fiber determinations, NDF and ADF do not measure the Citrus pulp 12 77 Soluble Rapid
more soluble fiber fractions of pectins and gums; therefore, they Corn bran 19 90 Insoluble Moderate
Guar gum 0 81 Soluble Rapid
are not widely used to determine fiber in pet foods. Gum arabic 0 91 Soluble Rapid
Pea fiber 30 92 Insoluble Moderate
Requirements Peanut hulls 57 76 Insoluble Slow
Rice bran 44 13 Insoluble Moderate
Fiber is not considered essential in the diets of cats and dogs, Soy fiber 20 83 Soluble Rapid
although it is often included in commercial foods. Overall, dogs Soy hulls 34 69 Insoluble Moderate/slow
and cats do not derive much energy from absorbing the typical Sunflower hulls 54 80 Insoluble Slow
Wheat bran 10 43 Insoluble Moderate
end products of bacterial fermentation; however, short-chain Wheat middlings 7 46 Insoluble Moderate
fatty acids are important in maintaining colonic health. *As is basis.
Therefore, a small amount of fiber (<5%) that contains both
rapidly and slowly fermentable fibers is recommended in foods
for healthy pets (Chapters 13 and 20). Today, much interest sources of fiber in dry extruded foods. Some pet foods contain
exists in human and veterinary nutrition about the role of specific ingredients added to provide fiber. Fiber sources com-
“pharmacologic doses” of certain nutrients (e.g., fiber) in pre- monly used in pet foods today include the hulls from rice, soy-
venting chronic diseases (Box 5-7). beans, peanuts and oats,dried beet pulp, various vegetable gums,
Fiber also aids in managing diseases such as obesity, diabetes corn bran, wheat bran, rice bran, oat bran and more purified
mellitus, diarrhea, colitis and constipation. The types and fiber sources such as oligosaccharides, cellulose and soy fiber.
amounts of dietary fiber required to assist in the management of AAFCO publishes official definitions of fiber ingredients
these diseases can be found in Chapters 27, 29, 56, 62 and 64. (2007). Table 5-9 lists common fiber ingredients with fiber con-
tent and general classifications of solubility and fermentability.
Deficiencies
Total deficiency of fiber in typical pet foods is not a practical
problem because many ingredients contain some fiber. PROTEIN/AMINO ACIDS
Homemade foods, veterinary therapeutic foods made with
more refined ingredients and purified diets used in research Definition
studies can be extremely low in fiber. Some dietary fiber that Proteins are large, complex molecules composed of hundreds to
produces short-chain fatty acids is usually recommended. thousands of amino acids. Amino acids are composed of car-
bon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and sometimes sulfur and
Excess/Toxicity phosphorus. Four chemical groups covalently bonded to a car-
bon atom form the general structure of amino acids. The four
Excess fiber may have undesirable effects. For instance, certain
groups include a hydrogen atom, a carboxyl group (COOH),
fiber types decrease mineral absorption. The effects on mineral
an α-amino group (NH ) and another chemical group specif-
2
absorption vary by type of fiber and the mineral. More rapidly
ic for each amino acid (Table 5-10). Although hundreds of
fermentable fibers (e.g., pectins and guar gum) appear to amino acids exist in nature, only 20 are commonly found as
decrease availability of some minerals, whereas fibers that con- protein components. The amino acids found in mammalian
tain more cellulose have little effect on mineral absorption. proteins are the L-isomer of α-amino acids, which means the
Excess fiber can dilute the energy and nutrient content of the side chain unique to each amino acid is linked to the α-carbon
food to such an extent that an animal may have difficulty eat- atom in the L (levorotatory) position.
ing enough of the food to meet its needs. Controlled levels of
fiber are advantageous in weight-reducing foods for dogs and Structure
cats; however, such foods are fortified so that only total energy Proteins are linear polymers of amino acids in which the amino
intake is low and other nutrients are present in adequate group of one amino acid and the carboxyl group of another
amounts to meet daily requirements. amino acid are coupled together (peptide bond) (Figure 5-15).
Amino acids arranged in chains are referred to as peptides.Two
Sources bonded amino acids form a dipeptide, three a tripeptide and
The maximum crude fiber content of pet foods must be listed in more than three a polypeptide.
the guaranteed analysis section of pet food labels in the United Proteins can be described as having a primary, secondary, ter-
States. Most dog and cat foods have DM crude fiber contents tiary or quaternary structure. The primary structure of proteins
of less than 5%. The fiber in most pet foods comes from a vari- refers to the sequence (order) of amino acids along the polypep-
ety of ingredients. Grains such as whole corn and brown rice are tide chain. The secondary structure of proteins refers to the