Page 998 - Saunders Comprehensive Review For NCLEX-RN
P. 998
▪ Nausea and vomiting
▪ Epigastric or right upper quadrant abdominal pain
▪ Arthralgia and rashes (more likely with hepatitis B virus)
▪ Hepatomegaly
Icteric Phase
▪ Jaundice, which is best assessed in the sclera, nail beds, and mucous membranes
▪ Dark urine and pale stools
▪ Pruritus
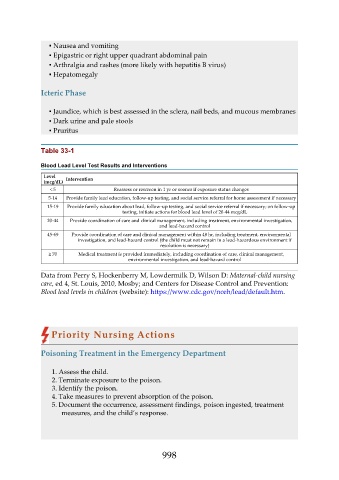
Table 33-1
Blood Lead Level Test Results and Interventions
Level Intervention
(mcg/dL)
< 5 Reassess or rescreen in 1 yr or sooner if exposure status changes
5-14 Provide family lead education, follow-up testing, and social service referral for home assessment if necessary
15-19 Provide family education about lead, follow-up testing, and social service referral if necessary; on follow-up
testing, initiate actions for blood lead level of 20-44 mcg/dL
20-44 Provide coordination of care and clinical management, including treatment, environmental investigation,
and lead-hazard control
45-69 Provide coordination of care and clinical management within 48 hr, including treatment, environmental
investigation, and lead-hazard control (the child must not remain in a lead-hazardous environment if
resolution is necessary)
≥ 70 Medical treatment is provided immediately, including coordination of care, clinical management,
environmental investigation, and lead-hazard control
Data from Perry S, Hockenberry M, Lowdermilk D, Wilson D: Maternal-child nursing
care, ed 4, St. Louis, 2010, Mosby; and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention:
Blood lead levels in children (website): https://www.cdc.gov/nceh/lead/default.htm.
Priority Nursing Actions
Poisoning Treatment in the Emergency Department
1. Assess the child.
2. Terminate exposure to the poison.
3. Identify the poison.
4. Take measures to prevent absorption of the poison.
5. Document the occurrence, assessment findings, poison ingested, treatment
measures, and the child’s response.
998