Page 7 - GP Spring 2025
P. 7
Together, these facts support the premise that a dental treatment can have an influence on a medical symptom:
1. The ears and oral cavity are in close proximity.
2. Crowns, fillings, and chronic, transient and acute malocclusions can impact tinnitus. 12
3. Moving teeth leads to changes in the muscles, gingiva, joints, sinuses and osseous substructures.
4. Moving teeth will have a neutral and/or positive and/or negative impact upon tinnitus.
5. Researchers have chronicled that orthodontics leaves one with a stable dentition less than half the time. 13
6. Relapse and malocclusion years after orthodontic care are not uncommon. 14
Medical visits for tinnitus (U.S.) and with orthodontists (U.S.) had large increases over 35+ year time periods (each > 600% when com-
pared to U.S. population growth).
Further research into the dentistry-tinnitus association would be prudent. Until it is determined that dentistry has no connection with unde-
sirable tinnitus consequences, it would be wise to incorporate steps expected to reduce negative impacts from moving teeth.
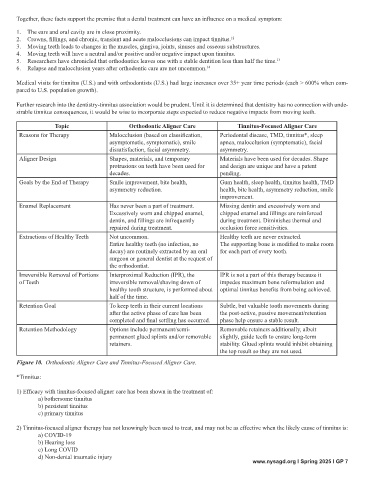
Topic Orthodontic Aligner Care Tinnitus-Focused Aligner Care
Reasons for Therapy Malocclusion (based on classification, Periodontal disease, TMD, tinnitus*, sleep
asymptomatic, symptomatic), smile apnea, malocclusion (symptomatic), facial
dissatisfaction, facial asymmetry. asymmetry.
Aligner Design Shapes, materials, and temporary Materials have been used for decades. Shape
protrusions on teeth have been used for and design are unique and have a patent
decades. pending.
Goals by the End of Therapy Smile improvement, bite health, Gum health, sleep health, tinnitus health, TMD
asymmetry reduction. health, bite health, asymmetry reduction, smile
improvement.
Enamel Replacement Has never been a part of treatment. Missing dentin and excessively worn and
Excessively worn and chipped enamel, chipped enamel and fillings are reinforced
dentin, and fillings are infrequently during treatment. Diminishes thermal and
repaired during treatment. occlusion force sensitivities.
Extractions of Healthy Teeth Not uncommon. Healthy teeth are never extracted.
Entire healthy teeth (no infection, no The supporting bone is modified to make room
decay) are routinely extracted by an oral for each part of every tooth.
surgeon or general dentist at the request of
the orthodontist.
Irreversible Removal of Portions Interproximal Reduction (IPR), the IPR is not a part of this therapy because it
of Teeth irreversible removal/shaving down of impedes maximum bone reformulation and
healthy tooth structure, is performed about optimal tinnitus benefits from being achieved.
half of the time.
Retention Goal To keep teeth in their current locations Subtle, but valuable tooth movements during
after the active phase of care has been the post-active, passive movement/retention
completed and final settling has occurred. phase help ensure a stable result.
Retention Methodology Options include permanent/semi- Removable retainers additionally, albeit
permanent glued splints and/or removable slightly, guide teeth to ensure long-term
retainers. stability. Glued splints would inhibit obtaining
the top result so they are not used.
Figure 10. Orthodontic Aligner Care and Tinnitus-Focused Aligner Care.
*Tinnitus:
1) Efficacy with tinnitus-focused aligner care has been shown in the treatment of:
a) bothersome tinnitus
b) persistent tinnitus
c) primary tinnitus
2) Tinnitus-focused aligner therapy has not knowingly been used to treat, and may not be as effective when the likely cause of tinnitus is:
a) COVID-19
b) Hearing loss
c) Long COVID
d) Non-dental traumatic injury
www.nysagd.org l Spring 2025 l GP 7