Page 384 - Beginning PHP 5.3
P. 384
Part III: Using PHP in Practice
String Data Types
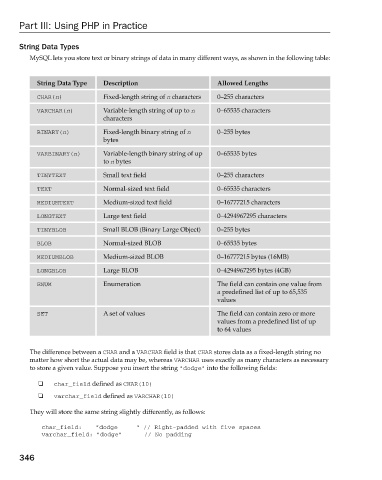
MySQL lets you store text or binary strings of data in many different ways, as shown in the following table:
String Data Type Description Allowed Lengths
CHAR( n ) Fixed - length string of n characters 0 – 255 characters
VARCHAR( n Variable - length string of up to n 0 – 65535 characters
)
characters
BINARY( n Fixed - length binary string of n 0 – 255 bytes
)
bytes
VARBINARY( n Variable - length binary string of up 0 – 65535 bytes
)
to n bytes
TINYTEXT Small text field 0 – 255 characters
TEXT Normal - sized text field 0 – 65535 characters
MEDIUMTEXT Medium - sized text field 0 – 16777215 characters
LONGTEXT Large text field 0 – 4294967295 characters
TINYBLOB Small BLOB (Binary Large Object) 0 – 255 bytes
BLOB Normal - sized BLOB 0 – 65535 bytes
MEDIUMBLOB Medium - sized BLOB 0 – 16777215 bytes (16MB)
LONGBLOB Large BLOB 0 – 4294967295 bytes (4GB)
ENUM Enumeration The field can contain one value from
a predefined list of up to 65,535
values
SET A set of values The field can contain zero or more
values from a predefined list of up
to 64 values
The difference between a CHAR and a VARCHAR field is that CHAR stores data as a fixed - length string no
matter how short the actual data may be, whereas VARCHAR uses exactly as many characters as necessary
to store a given value. Suppose you insert the string “ dodge ” into the following fields:
❑ char_field defined as CHAR(10)
❑ varchar_field defined as VARCHAR(10)
They will store the same string slightly differently, as follows:
char_field: “dodge “ // Right-padded with five spaces
varchar_field: “dodge” // No padding
346
9/21/09 9:11:09 AM
c12.indd 346
c12.indd 346 9/21/09 9:11:09 AM