Page 135 - The Manga Guide to Biochemistry
P. 135
You got it!
First, the fatty acid is activated by the attachment of CoA. This fatty acid–CoA
compound is called acyl-CoA. A carnitine is then added to form acyl-carnitine, which
is shuttled into the cell. It then enters the mitochondrion and is broken down into
acetyl-CoA.
Fatty acids are long carbon chains (10+), but acetyl-CoA has only two carbon
atoms.
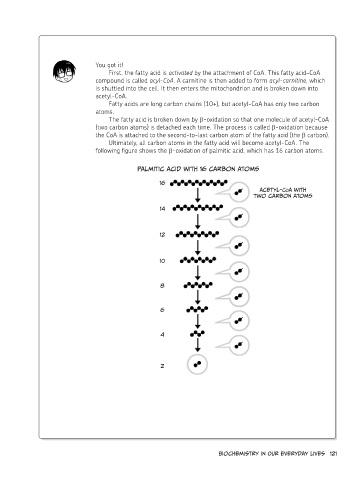
The fatty acid is broken down by β-oxidation so that one molecule of acetyl-CoA
(two carbon atoms) is detached each time. The process is called β-oxidation because
the CoA is attached to the second-to-last carbon atom of the fatty acid (the β carbon).
Ultimately, all carbon atoms in the fatty acid will become acetyl-CoA. The
following figure shows the β-oxidation of palmitic acid, which has 16 carbon atoms.
Palmitic acid with 16 carbon atoms
16
Acetyl-CoA with
two carbon atoms
14
12
10
8
6
4
2
Biochemistry in Our Everyday Lives 121