Page 492 - The ROV Manual - A User Guide for Remotely Operated Vehicles 2nd edition
P. 492
18.2 Metal object detection 487
(a)
12 34
FIGURE 18.12
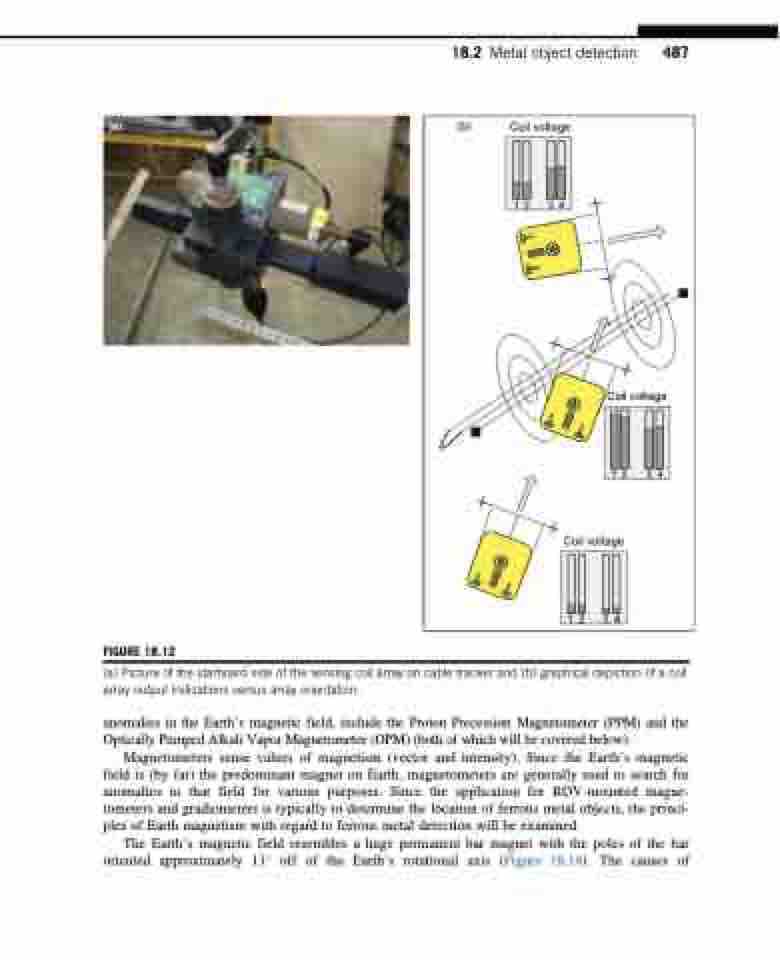
(a) Picture of the starboard side of the sensing coil array on cable tracker and (b) graphical depiction of a coil array output indications versus array orientation.
anomalies in the Earth’s magnetic field, include the Proton Precession Magnetometer (PPM) and the Optically Pumped Alkali Vapor Magnetometer (OPM) (both of which will be covered below).
Magnetometers sense values of magnetism (vector and intensity). Since the Earth’s magnetic field is (by far) the predominant magnet on Earth, magnetometers are generally used to search for anomalies in that field for various purposes. Since the application for ROV-mounted magne- tometers and gradiometers is typically to determine the location of ferrous metal objects, the princi- ples of Earth magnetism with regard to ferrous metal detection will be examined.
The Earth’s magnetic field resembles a huge permanent bar magnet with the poles of the bar oriented approximately 11 off of the Earth’s rotational axis (Figure 18.14). The causes of
(b) Coil voltage
Coil voltage
12 34
Coil voltage
12 34