Page 59 - The ROV Manual - A User Guide for Remotely Operated Vehicles 2nd edition
P. 59
2.3 Ocean dynamics 47
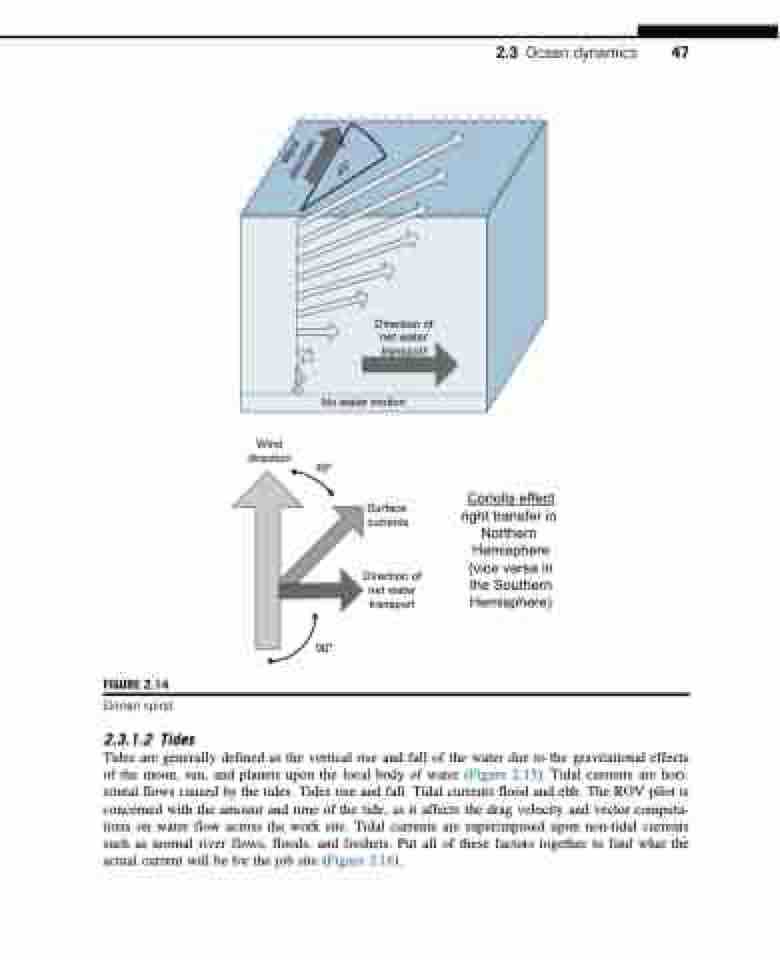
Direction of net water transport
No water motion
Wind
direction
45°
Surface currents
Direction of net water transport
Coriolis effect right transfer in Northern
Hemisphere (vice versa in the Southern Hemisphere)
FIGURE 2.14
Ekman spiral.
2.3.1.2 Tides
90°
Tides are generally defined as the vertical rise and fall of the water due to the gravitational effects of the moon, sun, and planets upon the local body of water (Figure 2.15). Tidal currents are hori- zontal flows caused by the tides. Tides rise and fall. Tidal currents flood and ebb. The ROV pilot is concerned with the amount and time of the tide, as it affects the drag velocity and vector computa- tions on water flow across the work site. Tidal currents are superimposed upon non-tidal currents such as normal river flows, floods, and freshets. Put all of these factors together to find what the actual current will be for the job site (Figure 2.16).
Wind direction
45°