Page 61 - The ROV Manual - A User Guide for Remotely Operated Vehicles 2nd edition
P. 61
2.3 Ocean dynamics 49
High water
Time (h)
High water
0 4 8 12 14 18 24
Low water
High water
Diurnal tide
High water
Semidiurnal tide
Lower high water
Semidiurnal mixed tide
High water
Time (h)
0 4 8 12 14 18 24
Low water
Low water
Higher high water
Higher high water
Higher low water
Time (h)
0 4 8 12 14Lower 18 24 low
water
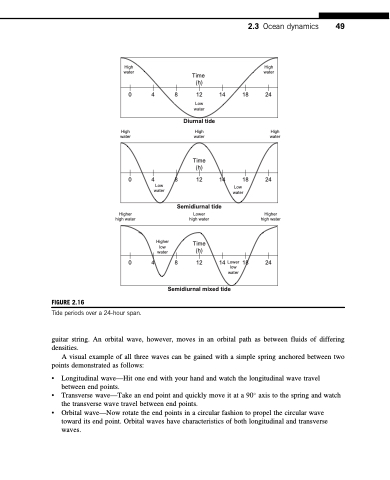
FIGURE 2.16
Tide periods over a 24-hour span.
guitar string. An orbital wave, however, moves in an orbital path as between fluids of differing densities.
A visual example of all three waves can be gained with a simple spring anchored between two points demonstrated as follows:
• Longitudinal wave—Hit one end with your hand and watch the longitudinal wave travel between end points.
• Transverse wave—Take an end point and quickly move it at a 90 axis to the spring and watch the transverse wave travel between end points.
• Orbital wave—Now rotate the end points in a circular fashion to propel the circular wave toward its end point. Orbital waves have characteristics of both longitudinal and transverse waves.