Page 84 - The ROV Manual - A User Guide for Remotely Operated Vehicles 2nd edition
P. 84
72 CHAPTER 3 Design Theory and Standards
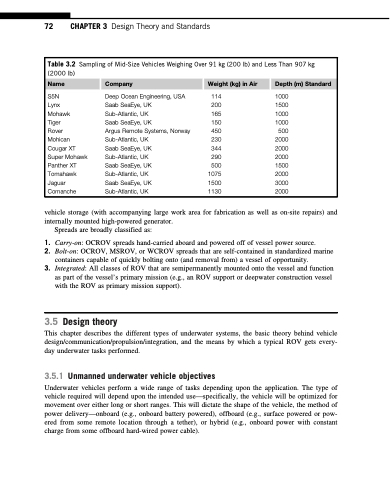
Table 3.2 Sampling of Mid-Size Vehicles Weighing Over 91 kg (200 lb) and Less Than 907 kg (2000 lb)
Name Company Weight (kg) in Air Depth (m) Standard
S5N
Lynx
Mohawk
Tiger
Rover
Mohican Cougar XT Super Mohawk Panther XT Tomahawk Jaguar Comanche
Deep Ocean Engineering, USA 114 1000 Saab SeaEye, UK 200 1500 Sub-Atlantic, UK 165 1000 Saab SeaEye, UK 150 1000 Argus Remote Systems, Norway 450 500 Sub-Atlantic, UK 230 2000 Saab SeaEye, UK 344 2000 Sub-Atlantic, UK 290 2000 Saab SeaEye, UK 500 1500 Sub-Atlantic, UK 1075 2000 Saab SeaEye, UK 1500 3000 Sub-Atlantic, UK 1130 2000
vehicle storage (with accompanying large work area for fabrication as well as on-site repairs) and internally mounted high-powered generator.
Spreads are broadly classified as:
1. Carry-on: OCROV spreads hand-carried aboard and powered off of vessel power source.
2. Bolt-on: OCROV, MSROV, or WCROV spreads that are self-contained in standardized marine
containers capable of quickly bolting onto (and removal from) a vessel of opportunity.
3. Integrated: All classes of ROV that are semipermanently mounted onto the vessel and function
as part of the vessel’s primary mission (e.g., an ROV support or deepwater construction vessel with the ROV as primary mission support).
3.5 Design theory
This chapter describes the different types of underwater systems, the basic theory behind vehicle design/communication/propulsion/integration, and the means by which a typical ROV gets every- day underwater tasks performed.
3.5.1 Unmanned underwater vehicle objectives
Underwater vehicles perform a wide range of tasks depending upon the application. The type of vehicle required will depend upon the intended use—specifically, the vehicle will be optimized for movement over either long or short ranges. This will dictate the shape of the vehicle, the method of power delivery—onboard (e.g., onboard battery powered), offboard (e.g., surface powered or pow- ered from some remote location through a tether), or hybrid (e.g., onboard power with constant charge from some offboard hard-wired power cable).