Page 1008 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1008
994 SECTION VIII Chemotherapeutic Drugs
in adult and juvenile rheumatoid arthritis and similar inflamma- Siltuximab is a Mab that binds to and blocks IL-6 from
tory diseases such as psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, binding to its cellular receptor. It is approved for the treatment
Crohn’s disease, and ulcerative colitis. of patients with multicentric Castleman’s disease who are HIV-
Abatacept and belatacept are recombinant fusion proteins negative and HHV-8-negative.
composed of the extracellular domain of cytotoxic T-lymphocyte- Tocilizumab is recombinant humanized IgG that binds to solu-
1
associated antigen 4 (CTLA-4) fused to the Fc domains of human ble and membrane-associated IL-6 receptors. It inhibits IL-6-medi-
IgG (Figure 55–7). Abatacept is approved for use in rheumatoid ated signaling on lymphocytes, suppressing inflammatory processes.
1
and other forms of arthritis and is discussed in Chapter 36. Belata- Similar to anti-TNF-α Mabs, patients receiving tocilizumab should
cept is approved to help prevent rejection in kidney transplants. be closely monitored for infectious diseases such as tuberculosis and
Both fusion proteins block the activation of T cells by binding other invasive bacterial, fungal, and viral infections.
CD80, blocking the CD28 activation signal in T cells. Basiliximab is a chimeric mouse-human IgG that binds
1
Anakinra is a recombinant form of the naturally occurring IL-1 to CD25, the IL-2 receptor α chain on activated lymphocytes.
receptor antagonist that prevents IL-1 from binding to its receptor, Daclizumab is a humanized IgG that also binds to the α subunit
1
stemming the cascade of cytokines that would otherwise be released. of the IL-2 receptor. Both agents function as IL-2 antagonists,
Anakinra is approved for use in adult rheumatoid arthritis patients blocking IL-2 from binding to activated lymphocytes, and are
who have failed treatment with one or more disease-modifying anti- therefore immunosuppressive. They are indicated for prophylaxis
rheumatic drugs. Rilonacept is a dimeric fusion protein consisting of acute organ rejection in renal transplant patients, and either
of the ligand-binding domains of the extracellular portions of the drug may be used as part of an immunosuppressive regimen that
human interleukin-1 receptor component (IL-1RI) and IL-1 recep- also includes glucocorticoids and cyclosporine.
tor accessory protein (IL-1RAcP) fused to the Fc portion of human Belimumab is a Mab that inhibits B cell activating factor, also
IgG . These molecules are indicated for treatment of cryopyrin- known as B lymphocyte stimulator, preventing B cells from being
1
associated periodic syndromes. stimulated. It is approved for treatment of adults with active,
Ixekizumab, secukinumab, and brodalumab are FDA- autoantibody-positive systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) who
approved for the treatment of patients with moderate to severe are also receiving standard therapy.
plaque psoriasis. Ixekizumab and secukinumab bind the IL-17 Canakinumab is a human IgG kappa chain monoclonal
cytokine and block it from binding to its receptor, while broda- antibody that prevents IL-1β from binding to its receptor. It is
lumab blocks IL-17 by binding to the IL-17 receptor itself. approved for cryopyrin-associated periodic syndromes (CAPS)
Reslizumab binds and neutralizes the biological activity of in adults and children 4 years old and older. CAPS includes
IL-5, thereby suppressing the production and survival of eosino- familial cold autoinflammatory syndrome, Muckle-Wells syn-
phils. It is approved for adult patients with severe eosinophilic drome, and systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis in children 2
asthma. Mepolizumab also binds to IL-5 and selectively inhibits years old or older. These diseases are caused by mutations in a
eosinophilic inflammation in patients with severe eosinophilic gene (NLRP-3) that encodes cryopyrin, an important compo-
asthma. nent of the inflammasome. NLRP-3 mutations cause excessive
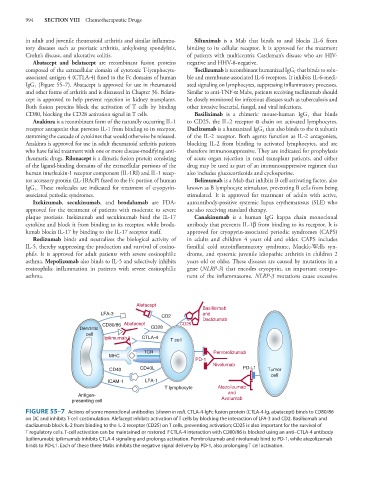
Alefacept
Basiliximab
LFA-3 and
CD2 Daclizumab
CD80/86 Abatacept CD25
Dendritic CD28
cell
Ipilimumab CTLA-4 T cell
TCR Pembrolizumab
MHC
PD-1
Nivolumab
CD40 CD40L PD-L1 Tumor
cell
ICAM-1 LFA-1
T lymphocyte Atezolizumab
and
Antigen-
presenting cell Avelumab
FIGURE 55–7 Actions of some monoclonal antibodies (shown in red). CTLA-4-lgFc fusion protein (CTLA-4-lg, abatacept) binds to CD80/86
on DC and inhibits T-cell costimulation. Alefacept inhibits activation of T cells by blocking the interaction of LFA-3 and CD2. Basiliximab and
daclizumab block IL-2 from binding to the IL-2 receptor (CD25) on T cells, preventing activation; CD25 is also important for the survival of
T regulatory cells. T-cell activation can be maintained or restored if CTLA-4 interaction with CD80/86 is blocked using an anti–CTLA-4 antibody
(ipilimumab); ipilimumab inhibits CTLA-4 signaling and prolongs activation. Pembrolizumab and nivolumab bind to PD-1, while atezolizumab
binds to PD-L1. Each of these three Mabs inhibits the negative signal delivery by PD-1, also prolonging T cell activation.