Page 1043 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1043
CHAPTER 57 Heavy Metal Intoxication & Chelators 1029
and the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) have advised A
pregnant women, women who might become pregnant, nursing O O
mothers, and young children to avoid consumption of fish with HO C C OH
high mercury levels (eg, swordfish) and to limit consumption of CH 2 CH 2
albacore tuna to 6 ounces a week, but to otherwise consume 8–12 N N
ounces of fish per week (see http://www.fda.gov/Food/Foodbor- CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2
neIllnessContaminants/Metals/ucm393070.htm).
Na O C C O Na
Treatment O O
A. Acute Exposure
O O
In addition to intensive supportive care, prompt chelation with
oral or intravenous unithiol, intramuscular dimercaprol, or oral B C O O C
succimer may be of value in diminishing nephrotoxicity after H C Ca CH 2
2
acute exposure to inorganic mercury salts. Vigorous hydration O N N O
may help to maintain urine output, but if acute renal failure
C
C
C
ensues, days to weeks of hemodialysis or hemodiafiltration in Na O C CH 2 H 2 H 2 H 2 C O Na
conjunction with chelation may be necessary. Because the efficacy
of chelation declines with time since exposure, treatment should
not be delayed until the onset of oliguria or other major systemic C O
effects. O
O O
O O
B. Chronic Exposure
Unithiol and succimer increase urine mercury excretion follow- Pb
ing acute or chronic elemental mercury inhalation, but the impact N
of such treatment on clinical outcome is unknown. Dimercaprol N
has been shown to redistribute mercury to the central nervous O
system from other tissue sites, and since the brain is a key target
organ, dimercaprol should not be used in treatment of exposure to
elemental or organic mercury. Limited data suggest that succimer,
unithiol, and N-acetyl-l-cysteine (NAC) may enhance body clear- O
ance of methylmercury.
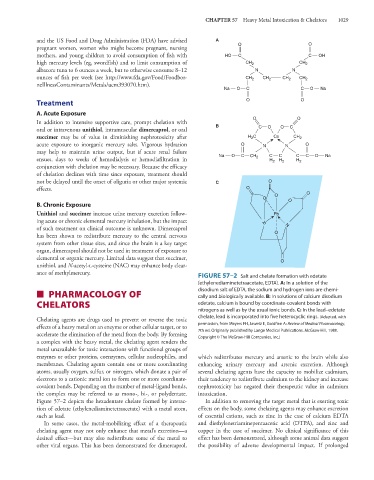
FIGURE 57–2 Salt and chelate formation with edetate
(ethylenediaminetetraacetate, EDTA). A: In a solution of the
■ PHARMACOLOGY OF disodium salt of EDTA, the sodium and hydrogen ions are chemi-
cally and biologically available. B: In solutions of calcium disodium
CHELATORS edetate, calcium is bound by coordinate-covalent bonds with
nitrogens as well as by the usual ionic bonds. C: In the lead–edetate
Chelating agents are drugs used to prevent or reverse the toxic chelate, lead is incorporated into five heterocyclic rings. (Adapted, with
effects of a heavy metal on an enzyme or other cellular target, or to permission, from Meyers FH, Jawetz E, Goldfien A: Review of Medical Pharmacology,
accelerate the elimination of the metal from the body. By forming 7th ed. Originally published by Lange Medical Publications. McGraw-Hill, 1980.
Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.)
a complex with the heavy metal, the chelating agent renders the
metal unavailable for toxic interactions with functional groups of
enzymes or other proteins, coenzymes, cellular nucleophiles, and which redistributes mercury and arsenic to the brain while also
membranes. Chelating agents contain one or more coordinating enhancing urinary mercury and arsenic excretion. Although
atoms, usually oxygen, sulfur, or nitrogen, which donate a pair of several chelating agents have the capacity to mobilize cadmium,
electrons to a cationic metal ion to form one or more coordinate- their tendency to redistribute cadmium to the kidney and increase
covalent bonds. Depending on the number of metal-ligand bonds, nephrotoxicity has negated their therapeutic value in cadmium
the complex may be referred to as mono-, bi-, or polydentate. intoxication.
Figure 57–2 depicts the hexadentate chelate formed by interac- In addition to removing the target metal that is exerting toxic
tion of edetate (ethylenediaminetetraacetate) with a metal atom, effects on the body, some chelating agents may enhance excretion
such as lead. of essential cations, such as zinc in the case of calcium EDTA
In some cases, the metal-mobilizing effect of a therapeutic and diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid (DTPA), and zinc and
chelating agent may not only enhance that metal’s excretion—a copper in the case of succimer. No clinical significance of this
desired effect—but may also redistribute some of the metal to effect has been demonstrated, although some animal data suggest
other vital organs. This has been demonstrated for dimercaprol, the possibility of adverse developmental impact. If prolonged