Page 276 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 276
262 SECTION III Cardiovascular-Renal Drugs
in systolic blood pressure of approximately 1 mm Hg after start-
ing sitagliptin. In one study, ipragliflozin resulted in an increase in
urine volume from day 1 to day 3. There was a 0.7-kg decrease in NH CH 2
body weight by day 3 compared to day 1. Both urine sodium and O
urine potassium excretion increased with the use of ipragliflozin, 4 3 2 1
but the serum concentrations of both electrolytes remained stable. Cl 5 6 COOH
Thus, it is likely that at least part of the weight loss is due to the
diuretic effect of the drugs. Recently there have also been reports H N O S
2
2
of acute kidney injury (AKI) with these drugs. At this point, it Furosemide
is unclear how much the diuretic and blood pressure-lowering
effects of these drugs contribute to the reported AKI. Cl Cl
SGLT2 inhibitor therapy is associated with a low incidence O
of hypoglycemia (3.5% versus 40.8% with glipizide). There is a
2
sixfold increased incidence of genital fungal infection in women H C C C O CH 2 COOH
and a slightly higher risk of urinary tract infections (8.8% versus C 2 5
H
6.1%). All of these agents have been shown to have no or minimal Ethacrynic acid
effects on serum electrolyte concentrations.
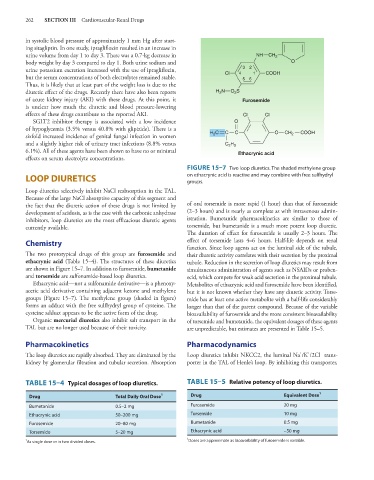
FIGURE 15–7 Two loop diuretics. The shaded methylene group
LOOP DIURETICS on ethacrynic acid is reactive and may combine with free sulfhydryl
groups.
Loop diuretics selectively inhibit NaCl reabsorption in the TAL.
Because of the large NaCl absorptive capacity of this segment and
the fact that the diuretic action of these drugs is not limited by of oral torsemide is more rapid (1 hour) than that of furosemide
development of acidosis, as is the case with the carbonic anhydrase (2–3 hours) and is nearly as complete as with intravenous admin-
inhibitors, loop diuretics are the most efficacious diuretic agents istration. Bumetanide pharmacokinetics are similar to those of
currently available. torsemide, but bumetanide is a much more potent loop diuretic.
The duration of effect for furosemide is usually 2–3 hours. The
Chemistry effect of torsemide lasts 4–6 hours. Half-life depends on renal
function. Since loop agents act on the luminal side of the tubule,
The two prototypical drugs of this group are furosemide and their diuretic activity correlates with their secretion by the proximal
ethacrynic acid (Table 15–4). The structures of these diuretics tubule. Reduction in the secretion of loop diuretics may result from
are shown in Figure 15–7. In addition to furosemide, bumetanide simultaneous administration of agents such as NSAIDs or proben-
and torsemide are sulfonamide-based loop diuretics. ecid, which compete for weak acid secretion in the proximal tubule.
Ethacrynic acid—not a sulfonamide derivative—is a phenoxy- Metabolites of ethacrynic acid and furosemide have been identified,
acetic acid derivative containing adjacent ketone and methylene but it is not known whether they have any diuretic activity. Torse-
groups (Figure 15–7). The methylene group (shaded in figure) mide has at least one active metabolite with a half-life considerably
forms an adduct with the free sulfhydryl group of cysteine. The longer than that of the parent compound. Because of the variable
cysteine adduct appears to be the active form of the drug. bioavailability of furosemide and the more consistent bioavailability
Organic mercurial diuretics also inhibit salt transport in the of torsemide and bumetanide, the equivalent dosages of these agents
TAL but are no longer used because of their toxicity. are unpredictable, but estimates are presented in Table 15–5.
Pharmacokinetics Pharmacodynamics
+
+
−
The loop diuretics are rapidly absorbed. They are eliminated by the Loop diuretics inhibit NKCC2, the luminal Na /K /2Cl trans-
kidney by glomerular filtration and tubular secretion. Absorption porter in the TAL of Henle’s loop. By inhibiting this transporter,
TABLE 15–4 Typical dosages of loop diuretics. TABLE 15–5 Relative potency of loop diuretics.
Drug Total Daily Oral Dose 1 Drug Equivalent Dose 1
Bumetanide 0.5–2 mg Furosemide 20 mg
Ethacrynic acid 50–200 mg Torsemide 10 mg
Furosemide 20–80 mg Bumetanide 0.5 mg
Torsemide 5–20 mg Ethacrynic acid ∼50 mg
1 1 Doses are approximate as bioavailability of furosemide is variable.
As single dose or in two divided doses.