Page 308 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 308
294 SECTION IV Drugs with Important Actions on Smooth Muscle
B. Organ System Effects action (Table 16–7). Because ergotamine dissociates very slowly
1. Central nervous system—As indicated by traditional from the α receptor, it produces very long-lasting agonist and
descriptions of ergotism, certain of the naturally occurring alka- antagonist effects at this receptor. There is little or no effect at β
loids are powerful hallucinogens. Lysergic acid diethylamide adrenoceptors.
(LSD; “acid”) is a synthetic ergot compound that clearly dem- Although much of the vasoconstriction elicited by ergot
onstrates this action. The drug has been used in the laboratory alkaloids can be ascribed to partial agonist effects at α adreno-
as a potent peripheral 5-HT antagonist, but good evidence sug- ceptors, some may be the result of effects at 5-HT receptors.
2
gests that its behavioral effects are mediated by agonist effects at Ergotamine, ergonovine, and methysergide all have partial agonist
prejunctional or postjunctional 5-HT receptors in the central effects at 5-HT vascular receptors. The remarkably selective
2
2
nervous system. In spite of extensive research, no clinical value has antimigraine action of the ergot derivatives was originally thought
been discovered for LSD’s dramatic central nervous system effects. to be related to their actions on vascular serotonin receptors. Cur-
Abuse of this drug has waxed and waned but is still widespread. It rent hypotheses, however, emphasize their action on prejunctional
is discussed in Chapter 32. neuronal 5-HT receptors.
Dopamine receptors in the central nervous system play After overdosage with ergotamine and similar agents, vasospasm
important roles in extrapyramidal motor control and the regu- is severe and prolonged (see Toxicity, below). This vasospasm is
lation of pituitary prolactin release. The actions of the peptide not easily reversed by α antagonists, serotonin antagonists, or
ergoline bromocriptine on the extrapyramidal system are dis- combinations of both.
cussed in Chapter 28. Of all the currently available ergot Ergotamine is typical of the ergot alkaloids that have a strong
derivatives, bromocriptine, cabergoline, and pergolide have the vasoconstrictor action. The hydrogenation of ergot alkaloids at
highest selectivity for the pituitary dopamine receptors. These the 9 and 10 positions (Table 16–6) yields dihydro derivatives
drugs directly suppress prolactin secretion from pituitary cells that have reduced serotonin partial agonist and vasoconstrictor
by activating regulatory dopamine receptors (see Chapter 37). effects and increased selective α-receptor-blocking actions.
They compete for binding to these sites with dopamine itself and 3. Uterine smooth muscle—The stimulant action of ergot
with other dopamine agonists such as apomorphine. They bind alkaloids on the uterus, as on vascular smooth muscle, appears
with high affinity and dissociate slowly. to combine α agonist, serotonin agonist, and other effects.
Furthermore, the sensitivity of the uterus to the stimulant
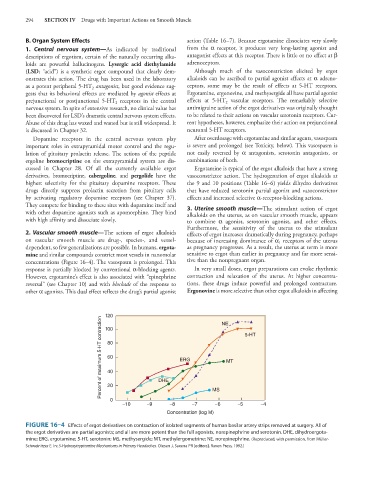
2. Vascular smooth muscle—The actions of ergot alkaloids effects of ergot increases dramatically during pregnancy, perhaps
on vascular smooth muscle are drug-, species-, and vessel- because of increasing dominance of α receptors of the uterus
1
dependent, so few generalizations are possible. In humans, ergota- as pregnancy progresses. As a result, the uterus at term is more
mine and similar compounds constrict most vessels in nanomolar sensitive to ergot than earlier in pregnancy and far more sensi-
concentrations (Figure 16–4). The vasospasm is prolonged. This tive than the nonpregnant organ.
response is partially blocked by conventional α-blocking agents. In very small doses, ergot preparations can evoke rhythmic
However, ergotamine’s effect is also associated with “epinephrine contraction and relaxation of the uterus. At higher concentra-
reversal” (see Chapter 10) and with blockade of the response to tions, these drugs induce powerful and prolonged contracture.
other α agonists. This dual effect reflects the drug’s partial agonist Ergonovine is more selective than other ergot alkaloids in affecting
120 NE 5-HT
Percent of maximum 5-HT contraction 80 ERG MT
100
60
40
20
0 DHE MS
−10 −9 −8 −7 −6 −5 −4
Concentration (log M)
FIGURE 16–4 Effects of ergot derivatives on contraction of isolated segments of human basilar artery strips removed at surgery. All of
the ergot derivatives are partial agonists; and all are more potent than the full agonists, norepinephrine and serotonin. DHE, dihydroergota-
mine; ERG, ergotamine; 5-HT, serotonin; MS, methysergide; MT, methylergometrine; NE, norepinephrine. (Reproduced, with permission, from Müller-
Schweinitzer E. In: 5-Hydroxytryptamine Mechanisms in Primary Headaches. Olesen J, Saxena PR [editors]. Raven Press, 1992.)