Page 420 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 420
406 SECTION V Drugs That Act in the Central Nervous System
Three stages of ethylene glycol overdose occur. Within the first with fomepizole is initiated immediately, as described above for
few hours after ingestion, there is transient excitation followed by methanol poisoning, and continued until the patient’s serum
CNS depression. After a delay of 4–12 hours, severe metabolic ethylene glycol concentration drops below a toxic threshold
acidosis develops from accumulation of acid metabolites and lac- (20–30 mg/dL). Intravenous ethanol is an alternative to fomepi-
tate. Finally, deposition of oxalate crystals in renal tubules occurs, zole in ethylene glycol poisoning. Hemodialysis effectively
followed by delayed renal insufficiency. The key to the diagnosis removes ethylene glycol and its toxic metabolites and is recom-
of ethylene glycol poisoning is recognition of anion gap acidosis, mended for patients with a serum ethylene glycol concentration
osmolar gap, and oxalate crystals in the urine in a patient without above 50 mg/dL, significant metabolic acidosis, and significant
visual symptoms. renal impairment. Fomepizole has reduced the need for hemo-
As with methanol poisoning, early fomepizole is the standard dialysis, especially in patients with less severe acidosis and intact
treatment for ethylene glycol poisoning. Intravenous treatment renal function.
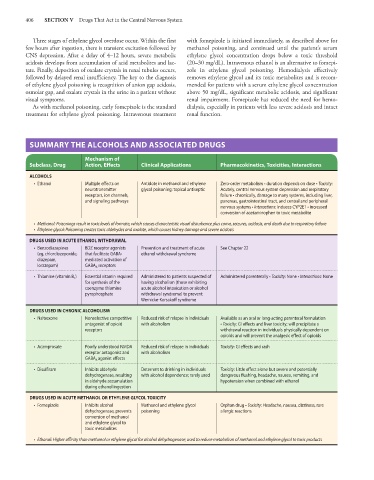
SUMMARY THE ALCOHOLS AND ASSOCIATED DRUGS
Mechanism of
Subclass, Drug Action, Effects Clinical Applications Pharmacokinetics, Toxicities, Interactions
ALCOHOLS
• Ethanol Multiple effects on Antidote in methanol and ethylene Zero-order metabolism • duration depends on dose • Toxicity:
neurotransmitter glycol poisoning; topical antiseptic Acutely, central nervous system depression and respiratory
receptors, ion channels, failure • chronically, damage to many systems, including liver,
and signaling pathways pancreas, gastrointestinal tract, and central and peripheral
nervous systems • Interactions: Induces CYP2E1 • increased
conversion of acetaminophen to toxic metabolite
• Methanol: Poisonings result in toxic levels of formate, which causes characteristic visual disturbance plus coma, seizures, acidosis, and death due to respiratory failure
• Ethylene glycol: Poisoning creates toxic aldehydes and oxalate, which causes kidney damage and severe acidosis
DRUGS USED IN ACUTE ETHANOL WITHDRAWAL
• Benzodiazepines BDZ receptor agonists Prevention and treatment of acute See Chapter 22
(eg, chlordiazepoxide, that facilitate GABA- ethanol withdrawal syndrome
diazepam, mediated activation of
lorazepam) GABA A receptors
• Thiamine (vitamin B 1 ) Essential vitamin required Administered to patients suspected of Administered parenterally • Toxicity: None • Interactions: None
for synthesis of the having alcoholism (those exhibiting
coenzyme thiamine acute alcohol intoxication or alcohol
pyrophosphate withdrawal syndrome) to prevent
Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome
DRUGS USED IN CHRONIC ALCOHOLISM
• Naltrexone Nonselective competitive Reduced risk of relapse in individuals Available as an oral or long-acting parenteral formulation
antagonist of opioid with alcoholism • Toxicity: GI effects and liver toxicity; will precipitate a
receptors withdrawal reaction in individuals physically dependent on
opioids and will prevent the analgesic effect of opioids
• Acamprosate Poorly understood NMDA Reduced risk of relapse in individuals Toxicity: GI effects and rash
receptor antagonist and with alcoholism
GABA A agonist effects
• Disulfiram Inhibits aldehyde Deterrent to drinking in individuals Toxicity: Little effect alone but severe and potentially
dehydrogenase, resulting with alcohol dependence; rarely used dangerous flushing, headache, nausea, vomiting, and
in aldehyde accumulation hypotension when combined with ethanol
during ethanol ingestion
DRUGS USED IN ACUTE METHANOL OR ETHYLENE GLYCOL TOXICITY
• Fomepizole Inhibits alcohol Methanol and ethylene glycol Orphan drug • Toxicity: Headache, nausea, dizziness, rare
dehydrogenase, prevents poisoning allergic reactions
conversion of methanol
and ethylene glycol to
toxic metabolites
• Ethanol: Higher affinity than methanol or ethylene glycol for alcohol dehydrogenase; used to reduce metabolism of methanol and ethylene glycol to toxic products