Page 486 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 486
472 SECTION V Drugs That Act in the Central Nervous System
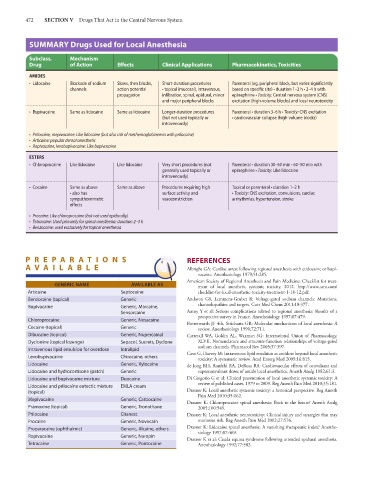
SUMMARY Drugs Used for Local Anesthesia
Subclass, Mechanism
Drug of Action Effects Clinical Applications Pharmacokinetics, Toxicities
AMIDES
• Lidocaine Blockade of sodium Slows, then blocks, Short-duration procedures Parenteral (eg, peripheral block, but varies significantly
channels action potential • topical (mucosal), intravenous, based on specific site) • duration 1–2 h • 2–4 h with
propagation infiltration, spinal, epidural, minor epinephrine • Toxicity: Central nervous system (CNS)
and major peripheral blocks excitation (high-volume blocks) and local neurotoxicity
• Bupivacaine Same as lidocaine Same as lidocaine Longer-duration procedures Parenteral • duration 3–6 h • Toxicity: CNS excitation
(but not used topically or • cardiovascular collapse (high-volume blocks)
intravenously)
• Prilocaine, mepivacaine: Like lidocaine (but also risk of methemoglobinemia with prilocaine)
• Articaine: popular dental anesthetic
• Ropivacaine, levobupivacaine: Like bupivacaine
ESTERS
• Chloroprocaine Like lidocaine Like lidocaine Very short procedures (not Parenteral • duration 30–60 min • 60–90 min with
generally used topically or epinephrine • Toxicity: Like lidocaine
intravenously)
• Cocaine Same as above Same as above Procedures requiring high Topical or parenteral • duration 1–2 h
• also has surface activity and • Toxicity: CNS excitation, convulsions, cardiac
sympathomimetic vasoconstriction arrhythmias, hypertension, stroke
effects
• Procaine: Like chloroprocaine (but not used epidurally)
• Tetracaine: Used primarily for spinal anesthesia; duration 2–3 h
• Benzocaine: used exclusively for topical anesthesia
PREP AR A TIONS REFERENCES
A V AIL ABLE Albright GA: Cardiac arrest following regional anesthesia with etidocaine or bupi-
vacaine. Anesthesiology 1979;51:285.
American Society of Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine: Checklist for treat-
GENERIC NAME AVAILABLE AS ment of local anesthetic systemic toxicity. 2012. http://www.asra.com/
Articaine Septocaine checklist-for-local-anesthetic-toxicity-treatment-1-18-12.pdf.
Benzocaine (topical) Generic Andavan GS, Lemmens-Gruber R: Voltage-gated sodium channels: Mutations,
Bupivacaine Generic, Marcaine, channelopathies and targets. Curr Med Chem 2011;18:377.
Sensorcaine Auroy Y et al: Serious complications related to regional anesthesia: Results of a
prospective survey in France. Anesthesiology 1997;87:479.
Chloroprocaine Generic, Nesacaine
Butterworth JF 4th, Strichartz GR: Molecular mechanisms of local anesthesia: A
Cocaine (topical) Generic review. Anesthesiology 1990;72:711.
Dibucaine (topical) Generic, Nupercainal Catterall WA, Goldin AL, Waxman SG: International Union of Pharmacology.
Dyclonine (topical lozenge) Sepacol, Sucrets, Dyclone XLVII. Nomenclature and structure-function relationships of voltage-gated
sodium channels. Pharmacol Rev 2005;57:397.
Intravenous lipid emulsion for overdose Intralipid
Cave G, Harvey M: Intravenous lipid emulsion as antidote beyond local anesthetic
Levobupivacaine Chirocaine, others
toxicity: A systematic review. Acad Emerg Med 2009;16:815.
Lidocaine Generic, Xylocaine de Jong RH, Ronfeld RA, DeRosa RA: Cardiovascular effects of convulsant and
Lidocaine and hydrocortisone (patch) Generic supraconvulsant doses of amide local anesthetics. Anesth Analg 1982;61:3.
Lidocaine and bupivacaine mixture Duocaine Di Gregorio G et al: Clinical presentation of local anesthetic systemic toxicity: A
review of published cases, 1979 to 2009. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2010;35:181.
Lidocaine and prilocaine eutectic mixture EMLA cream
(topical) Drasner K: Local anesthetic systemic toxicity: a historical perspective. Reg Anesth
Pain Med 2010;35:162.
Mepivacaine Generic, Carbocaine Drasner K: Chloroprocaine spinal anesthesia: Back to the future? Anesth Analg
Pramoxine (topical) Generic, Tronothane 2005;100:549.
Prilocaine Citanest Drasner K: Local anesthetic neurotoxicity: Clinical injury and strategies that may
Procaine Generic, Novocain minimize risk. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2002;27:576.
Proparacaine (ophthalmic) Generic, Alcaine, others Drasner K: Lidocaine spinal anesthesia: A vanishing therapeutic index? Anesthe-
siology 1997;87:469.
Ropivacaine Generic, Naropin Drasner K et al: Cauda equina syndrome following intended epidural anesthesia.
Tetracaine Generic, Pontocaine Anesthesiology 1992;77:582.