Page 597 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 597
CHAPTER 32 Drugs of Abuse 583
Opioids
MOR
GABA
Ca 2+ K +
DA VGCC Kir3
MOR
MOR
GABA Ca 2+ βγ βγ
THC
CB R
1
GABA
A
DA GABA R
GHB
GABA B
DA
GABA
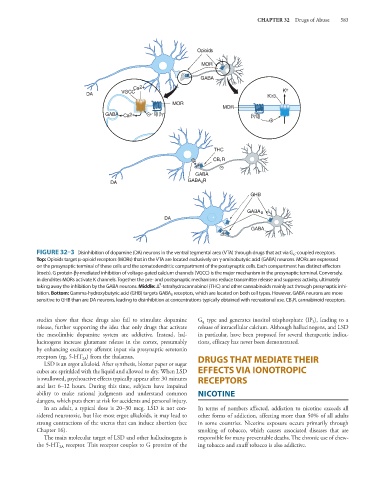
FIGURE 32–3 Disinhibition of dopamine (DA) neurons in the ventral tegmental area (VTA) through drugs that act via G io -coupled receptors.
Top: Opioids target μ-opioid receptors (MORs) that in the VTA are located exclusively on γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) neurons. MORs are expressed
on the presynaptic terminal of these cells and the somatodendritic compartment of the postsynaptic cells. Each compartment has distinct effectors
(insets). G protein-βγ-mediated inhibition of voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCC) is the major mechanism in the presynaptic terminal. Conversely,
in dendrites MORs activate K channels. Together the pre- and postsynaptic mechanisms reduce transmitter release and suppress activity, ultimately
9
taking away the inhibition by the GABA neurons. Middle: Δ -tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and other cannabinoids mainly act through presynaptic inhi-
bition. Bottom: Gamma-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB) targets GABA B receptors, which are located on both cell types. However, GABA neurons are more
sensitive to GHB than are DA neurons, leading to disinhibition at concentrations typically obtained with recreational use. CB 1 R, cannabinoid receptors.
studies show that these drugs also fail to stimulate dopamine G type and generates inositol trisphosphate (IP ), leading to a
q
3
release, further supporting the idea that only drugs that activate release of intracellular calcium. Although hallucinogens, and LSD
the mesolimbic dopamine system are addictive. Instead, hal- in particular, have been proposed for several therapeutic indica-
lucinogens increase glutamate release in the cortex, presumably tions, efficacy has never been demonstrated.
by enhancing excitatory afferent input via presynaptic serotonin
) from the thalamus.
receptors (eg, 5-HT 2A DRUGS THAT MEDIATE THEIR
LSD is an ergot alkaloid. After synthesis, blotter paper or sugar
cubes are sprinkled with the liquid and allowed to dry. When LSD EFFECTS VIA IONOTROPIC
is swallowed, psychoactive effects typically appear after 30 minutes RECEPTORS
and last 6–12 hours. During this time, subjects have impaired
ability to make rational judgments and understand common NICOTINE
dangers, which puts them at risk for accidents and personal injury.
In an adult, a typical dose is 20–30 mcg. LSD is not con- In terms of numbers affected, addiction to nicotine exceeds all
sidered neurotoxic, but like most ergot alkaloids, it may lead to other forms of addiction, affecting more than 50% of all adults
strong contractions of the uterus that can induce abortion (see in some countries. Nicotine exposure occurs primarily through
Chapter 16). smoking of tobacco, which causes associated diseases that are
The main molecular target of LSD and other hallucinogens is responsible for many preventable deaths. The chronic use of chew-
the 5-HT receptor. This receptor couples to G proteins of the ing tobacco and snuff tobacco is also addictive.
2A